Application of the CANARY event detection software for real-time performance monitoring of decentralized water reuse systems†
Abstract
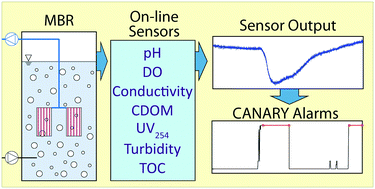
Real-time monitoring of water reuse systems ensures the production of high quality water to protect human health at the point-of-use. In this study, several online real-time sensors were utilized to monitor effluent from a wastewater fed laboratory-scale membrane bioreactor (MBR) under natural and simulated failure conditions. These simulated failures included adding reactor mixed liquor to emulate a membrane breach, and spiking MS2 bacteriophage into the reactor to create a high viral load, which might be observed during an outbreak. The CANARY event detection software was used to analyze sensor data and report changes in water quality that might be indicative of poor system behavior. During simulated failure conditions, CANARY reported 20 alarms, accurately detecting each failure. During natural operating conditions, 219 alarms were produced and 189 were attributed to known events (e.g., system and sensor maintenance). The remaining alarms (23) during natural operating conditions were considered to have an unknown cause. However, 13 of those had signal deviations similar to known events, but could not be definitively linked to a source. The results of this study suggest that real-time monitoring in conjunction with CANARY analysis may be useful as an early warning system for monitoring the effluent of water reuse systems, and may help to quickly identify treatment malfunctions or other abnormal conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...