Amino acid modified copper electrodes for the enhanced selective electroreduction of carbon dioxide towards hydrocarbons†
Abstract
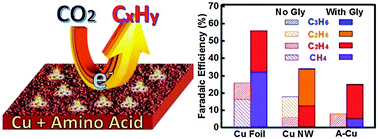
Electroreduction of carbon dioxide to hydrocarbons has been proposed as a promising way to utilize CO2 and maintain carbon balance in the environment. Copper (Cu) is an effective electrocatalyst for such a purpose. However, the overall selectivity towards hydrocarbons on Cu-based electrodes is still very limited. In this work, we develop a general amino acid modification approach on Cu electrodes for the selective electroreduction of CO2 towards hydrocarbons. A remarkable enhancement in hydrocarbon generation is achieved on these modified copper electrodes, regardless of the morphology of the Cu electrodes. A density functional theory calculation reveals that the key intermediate CHO* is stabilized by interacting with –NH3+ of the adsorbed zwitterionic glycine. Our results suggest that amino acids and their derivatives are promising modifiers in improving the selectivity of hydrocarbons in CO2 electroreduction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...