Improvement in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy from cubic SiC semiconductor nanowhiskers by adjustment of energy levels†
Abstract
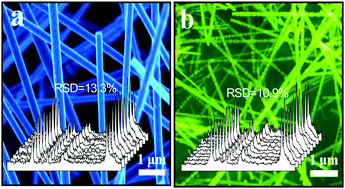
Enhanced reproducible Raman signals of the 4-MBA molecule were observed on the surface of semiconducting SiC nanowhiskers (SiCNWs) by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). The SERS enhancement was further tuned and boosted by doping with B. Theoretical calculations were performed to unravel the mechanism of the SERS enhancement and it was found that the SERS effect was strongly associated with the energy level structure between the substrate and analyte. Appropriate energy level matching facilitated the charge transfer process during laser illumination, enhancing the SERS signal. This proposed mechanism was verified through multiple control experiments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...