Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) formation from benzyl radicals: a reaction kinetics study†
Abstract
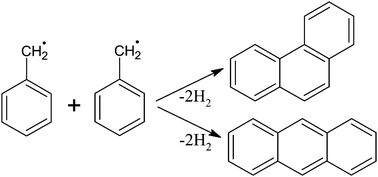
The role of resonantly stabilized radicals such as propargyl, cyclopentadienyl and benzyl in the formation of aromatic hydrocarbons such as benzene and naphthalene in the high temperature environments has been long known. In this work, the possibility of benzyl recombination to form three-ring aromatics, phenanthrene and anthracene, is explored. A reaction mechanism for it is developed, where reaction energetics are calculated using density functional theory (B3LYP functional with 6-311++G(d,p) basis set) and CBS-QB3, while temperature-dependent reaction kinetics are evaluated using transition state theory. The mechanism begins with barrierless formation of bibenzyl from two benzyl radicals with the release of 283.2 kJ mol−1 of reaction energy. The further reactions involve H-abstraction by a H atom, H-desorption, H-migration, and ring closure to gain aromaticity. Through mechanism and rate of production analyses, the important reactions leading to phenanthrene and anthracene formation are determined. Phenanthrene is found to be the major product at high temperatures. Premixed laminar flame simulations are carried out by including the proposed reactions for phenanthrene formation from benzyl radicals and compared to experimentally observed species profiles to understand their effects on species concentrations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...