Surface modified multifunctional ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles for hydrophobic and hydrophilic anti-cancer drug molecule loading†
Abstract
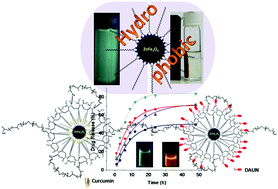
Multifunctional ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles were successfully synthesized via thermolysis of Fe-oleate and Zn-oleate precursors. Monodisperse, single phase ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles with an average particle size of ∼22 nm, exhibiting green emission (λmax ∼ 480 nm) and ferromagnetism at room temperature (saturation magnetization of 48.46 emu gm−1) have been formed by this novel approach. By appropriate surface functionalization, these materials have been converted into smart carriers of hydrophobic (water insoluble) drug molecule-curcumin and hydrophilic (water soluble) drug molecule-daunorubicin. The in vitro cytotoxicity of both the hydrophobic and hydrophilic drug loaded ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles was studied using the conventional MTT assay which revealed that the drug loaded nanoparticles induce significant death of the carcinoma cells (HeLa). Interestingly, this appears to be a significant development towards the capability of surface functionalized multifunctional ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles as carriers for both water soluble and insoluble drugs for anti-cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...