Mechanism for the photoreduction of poly(vinylpyrrolidone) to HAuCl4 and the dominating saturable absorption of Au colloids
Abstract
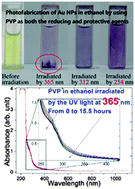
Both fabrication of Au nano-objects and the nonlinear optical properties of Au nano-objects are the focus of research. In the present work, Au nanoparticles with different mean sizes (18, 32, 42, and 70 nm) are controllably fabricated in ethanol by changing the concentration of poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP) and HAuCl4, as well as the power of continuous wave UV light at 365 nm. PVP acts as both reducing and protective agent. The mechanism of photoreduction of PVP to HAuCl4 is proposed. PVP undergoes a series of chemical reactions which include the attack of the hydrogen atom on the tertiary carbon atom at the α-position of the nitrogen atom, production of a hydroxyl radical, and chain scission. The hydroxyl radical combines with the hydrogen atom produced through the dissociation of HAuCl4, which facilitates the decomposition of HAuCl4. The fabrication mechanism of Au nanoparticles is discussed. The nonlinear absorption of these Au nanoparticles is investigated; all of them exhibit saturable absorption, and the saturable absorption dominates the nonlinear absorption with the increase of laser energy. The dominance of saturable absorption in the nonlinear absorption is due to the stronger single-photon absorbed intraband absorption from the ground state to the first excited state in the conduction band, the weaker excited state absorption in the conduction band, and the weaker two-photon absorption from the d band to the conduction band.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...