A series of dinuclear cuprous iodide complexes chelated with 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)benzene derivatives: structural, photophysical and thermal properties†
Abstract
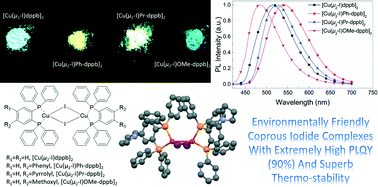
Three new bisphosphine ligands, 4-phenyl-1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)benzene (Ph-dppb), 4-pyrrolyl-1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)benzene (Pr-dppb), and 4,5-dimethoxyl-1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)benzene (OMe-dppb), were synthesized to coordinate with cuprous iodide (CuI), and compared with 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)benzene (dppb). Single crystal X-ray diffraction and elemental analysis experiments indicate that three binuclear CuI complexes with formulae of [Cu(μ2-I)Ph-dppb]2, [Cu(μ2-I)Pr-dppb]2, and [Cu(μ2-I)OMe-dppb]2 were obtained, which are the same as the reference complex [Cu(μ2-I)dppb]2. The three complexes showed a maximum emission band (λmax) in the range of 484–535 nm which varies in the electron effect of the substituted groups (i.e. methoxy, pyrrolyl, phenyl) on [Cu(μ2-I)dppb]2, and in high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) from 53 to 90% in the solid state. Furthermore, the complexes [Cu(μ2-I)Ph-dppb]2 and [Cu(μ2-I)Pr-dppb]2 exhibited a thermal decomposition temperature exceeding 380 °C. The high PLQY and excellent thermal stability of these CuI complexes imply their great potential application as efficient emitters in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs).
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2016 New talent

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...