Thermal, electrical and structural studies on ionic liquid confined in ordered mesoporous MCM-41
Abstract
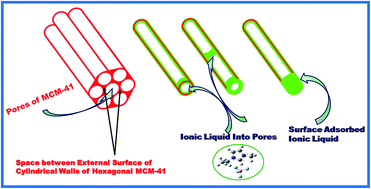
In the present study, immobilization of different amounts of ionic liquid (IL) 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium tetrafluoroborate [EMIM][BF4] into the pores of ordered mesoporous MCM-41 (Mobil Composition of Matter no. 41) has been accomplished successfully. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and dielectric spectroscopy results indicate the presence of surface adsorbed IL besides, IL confined in pores. The IL adsorbed on the surface of MCM-41 has been removed after washing. DSC and dielectric spectroscopy results and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) confirm the removal of the surface adsorbed IL. Glass transition temperature (Tg) and thermal stability have been found to change as compared to the bulk IL in confinement. An FTIR study shows that the vibrational bands related to the ring of the IL cation shift upon confinement due to the interaction between oxygen of the silica pore wall surface and C–H of the cation ring. Anion [BF4]− also interacts with the pore wall as confirmed experimentally and theoretically. Fluorescence spectra of IL show the blue shift upon incorporation into the ordered mesoporous MCM-41.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...