An experimental study on the effects of temperature and magnetic field strength on the magnetorheological fluid stability and MR effect
Abstract
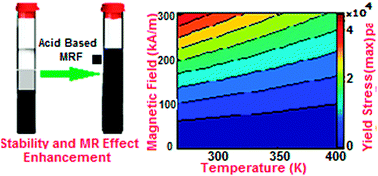
In this study, the stability and rheological properties of a suspension of carbonyl iron microparticles (CIMs) in silicone oil were investigated within a temperature range of 10 to 85 °C. The effect of adding two hydrophobic (stearic and palmitic) acids on the stability and magnetorheological effect of a suspension of CIMs in silicone oil was studied. According to the results, for preparing a stable and efficient magnetorheological (MR) fluid, additives should be utilized. Therefore, 3 wt% of stearic acid was added to the MR fluid which led to an enhancement of the fluid stability over 92% at 25 °C. By investigating shear stress variation due to the changes in the shear rate for acid-based MR fluids, the maximum yield stress was obtained by fitting the Bingham plastic rheological model at high shear rates. Based on the existing correlations of yield stress and either temperature or magnetic field strength, a new model was fitted to the experimental data to monitor the simultaneous effect of magnetic field strength and temperature on the maximum yield stress. The results demonstrated that as the magnetic field intensified or the temperature decreased, the maximum yield stress increased dramatically. In addition, when the MR fluid reached its magnetic saturation, the viscosity of fluid depended only on the shear rate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...