Novel modified magnetic nanocomposite for determination of trace amounts of lead ions
Abstract
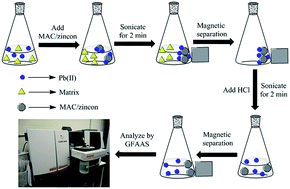
A procedure for the analysis of trace amount of Pb(II) by magnetic activated carbon modified with zincon (MAC/zincon) has been proposed. The prepared magnetic nanocomposite was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The experimental factors affecting the extraction efficiency such as pH, zincon amount, extraction and desorption time, concentration of eluent, sample volume and influence of coexisting ions were systematically examined. Under the optimized conditions, the limit of detection (LOD, 3Sb) and the relative standard deviation (RSD, n = 6, c = 50 ng L−1) were 7.2 ng L−1 and 4.9%, respectively. The maximum sorption capacity of the adsorbent for Pb(II) was found to be 28.4 mg g−1. An enrichment factor (EF) of 200 was achieved using this method. Finally, the method was successfully applied to monitoring lead in human hair, vegetable and water samples with recoveries in the range of 96.0–103.5% for the spiked samples. The fast extraction ability of the magnetic nanocomposite makes it a promising sorbent for various solid phase extractions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...