Multifunctional polymers with biomimetic compound architectures via nanoporous AAO films for efficient solar energy harvesting in dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
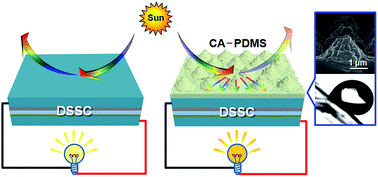
We report the considerable enhancement of the solar power conversion efficiency (PCE) in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) patterned with a novel biomimetic compound architecture (CA) (i.e., hierarchical nanobumps/microcone arrays) with light-harvesting and self-cleaning functions as a protective cover-layer. The CA-PDMS is transferred from a nanoporous anodic alumina oxide mold by a facile and cost-effective soft imprint lithography via a microcone-patterned sapphire substrate. A lamination of CA-PDMS on the glass leads to increased total and diffuse transmittance properties (i.e., antireflection and light scattering effects), simultaneously, compared to bare glass over a wide wavelength range of 350–800 nm, exhibiting a much larger solar weighted total transmittance (TSW) value of ∼94% and an average haze ratio (HA) value of ∼49.7% (TSW ≈ 90.4% and HA ≈ 1.4% for bare glass). In addition, sand grains on the hydrophobic surface with a water contact angle of ∼134° are clearly washed by rolling down water droplets (i.e., self-cleaning effect). To simply demonstrate the device applicability, CA-PDMS is introduced onto an outer surface of the front glass substrate in a DSSC. The resulting DSSC with CA-PDMS exhibits a boosted PCE value of ∼8.24% mainly due to a strongly increased short-circuit current density (JSC) value of ∼18.11 mA cm−2 compared to the reference DSSC with bare glass (PCE ≈ 7.45% and JSC ≈ 16.37 mA cm−2) under AM1.5G illumination, indicating a large PCE enhancement percentage value of ∼10.7%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...