Synthesis, in silico screening and preclinical evaluation studies of a hexapeptide analogue for its antimicrobial efficacy†
Abstract
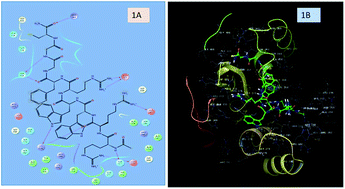
A novel Trp-Arg rich antimicrobial peptide was designed and the synthesized nonapeptide (hexapeptide analogue AMP) was screened for its antimicrobial and hemolytic activity. In silico studies were performed against a microbial target protein to validate the findings. In vivo studies were carried out for preclinical evaluation of the designed peptide sequence using 99mTc as the radioisotope. The results obtained from the in vitro studies revealed excellent antibacterial activity against E. coli with low hemolytic activity. The in silico studies with the crystal structure of E. coli Pencillin Binding Protein 1b (PBP1b) glycosyltransferase (PDB ID: 3VMA) show higher electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions than the co-crystallized ligand. The radio labeling yield of the 99mTc-labeled AMP was found to be >98%. The blood-kinetics in rabbits and the biodistribution studies in mice confirmed rapid renal excretion from systemic circulation. The scintigraphic analysis for the infection and inflammation animal models revealed that the radiolabel was able to discriminate between infection and inflammation in both mice and rats. Furthermore, blocking experiments in scintigraphy were also carried out using cold peptide to confirm the specificity towards the E. coli infection. Based on the above findings, we consider the designed AMP as a novel antimicrobial agent with the ability to image bacterial infection in vivo by using a gamma emitting radioisotope.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...