Influence of the diversified structural variations at the imine functionality of 4-bromophenylacetic acid derived hydrazones on alkaline phosphatase inhibition: synthesis and molecular modelling studies†‡
Abstract
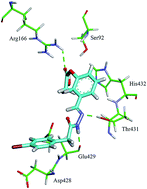
Alkaline phosphatase (AP) isozymes are present in a wide range of species from bacteria to humans with an ability to dephosphorylate and transphosphorylate a wide range of substrates. In humans, four AP isozymes have been identified such as tissue-nonspecific (TNAP), intestinal (IAP), placental (PLAP) and germ cell (GCAP) APs. Modulation of the activity of the different AP isozymes may have therapeutic implications in distinct diseases and cellular processes. To identify potent inhibitors of APs, a diverse range of 4-bromophenylacetic acid derived hydrazone derivatives has been synthesized and characterized by spectro-analytical methods and, in the case of 4i and 4q, by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. Among the tested series, several compounds were identified as lead candidates showing IC50 values from micro to nanomolar ranges. Compound 4k displayed exceptional activity with an IC50 value of 10 nM against h-IAP. This inhibitory effect is ∼10 000-fold more potent than the standard drug L-phenylalanine. Compounds 4p, 4g and 4e were potent inhibitors of TNAP, PLAP and GCAP, respectively. Molecular docking studies of the respective potent inhibitors have been carried out to rationalize the important binding modes of the most active inhibitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...