Identification of MRC2 and CD209 receptors as targets for photodynamic therapy of retinoblastoma using mesoporous silica nanoparticles†
Abstract
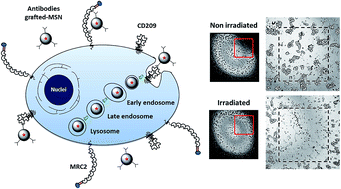
Research in nanomedicine has grown rapidly over the past few years and is playing a key role in the development of effective treatments for ophthalmological purpose. Retinoblastoma is an intraocular tumor triggered by genetic mutation in young children and photodynamic therapy (PDT) is currently developed as a promising non-mutagenic approach to treat this cancer. In this work, we have first identified two receptors, MRC2 and CD209, which are highly expressed by retinoblastoma. Then, we developed mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) grafted with the antibodies anti-MRC2 and/or anti-CD209 for retinoblastoma PDT and imaging.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...