Fabrication of nickel oxide nanostructures with high surface area and application for urease-based biosensor for urea detection†
Abstract
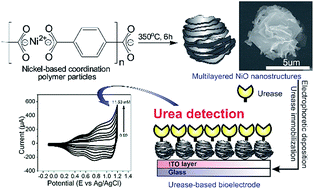
Uniform nanostructured nickel-based coordination polymer particles with multilayered morphologies (mL-NiCPPs) were successfully fabricated through a two-step heating process. To increase the surface area by reducing the size of mL-NiCPPs, pyridine and acetic acid were added as size modulators during the growth process. The resultant coordination polymer nanoparticles were then calcinated at a controlled temperature in order to produce nickel oxide nanostructures (mL-NiOs), which have a regular multilayered morphology and a high degree of crystallinity. Moreover, the mL-NiOs had a relatively high BET specific surface area (112 m2 g−1) and a well-defined pore size (10 nm), hence exhibited significant potential for use in a variety of applications. The synthesized mL-NiOs were successfully deposited onto indium tin oxide (ITO) serving as an efficient matrix for the immobilization of urease (Ur), which was used for urea detection. The prepared bioelectrode (Ur/NiO/ITO/glass) was employed for urea sensing using cyclic voltammetry (CV). The prepared electrodes showed a high sensitivity and a linear dependence of the current on the urea concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...