New aryloxy-quinone derivatives as potential anti-Chagasic agents: synthesis, trypanosomicidal activity, electrochemical properties, pharmacophore elucidation and 3D-QSAR analysis†
Karina Vázqueza,
Christian Espinosa-Bustosa,
Jorge Soto-Delgadob,
Ricardo A. Tapiaa,
Javier Varelac,
Estefanía Birrielc,
Rodrigo Segurad,
Jaime Pizarrod,
Hugo Cerecettoce,
Mercedes Gonzálezc,
Margot Paulino*f and
Cristian O. Salas*a
aDepartamento de Química Orgánica, Facultad de Química, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago 6094411, Chile. E-mail: cosalas@uc.cl
bDepartamento de Ciencias Químicas, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Universidad Andrés Bello, Quillota 980, Viña del Mar, Chile
cGrupo de Química Medicinal, Instituto de Química Biológica, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de la República, Iguá 4225, Montevideo, Uruguay
dDepartamento de Química de los Materiales, Facultad de Química y Biología, Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Santiago 9170022, Chile
eÁrea de Radiofarmacia, Centro de Investigaciones Nucleares, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de la República, Mataojo 2055, Montevideo, Uruguay
fCentro de Bioinformática Estructural-DETEMA, Facultad de Química, Universidad de la República, C.C. 1157, Montevideo, Uruguay. E-mail: margot@fq.edu.uy
First published on 22nd July 2015
Abstract
A set of new aryloxy-quinones were synthesized and evaluated in vitro against the epimastigote form of Trypanosoma cruzi and their unspecific cytotoxicity was tested on murine macrophages J-774 cells. Most of these novel compounds were found to be much more potent and selective than the standard drug nifurtimox. Interestingly, 2-phenoxy-naphthoquinone 3b displayed a remarkable nanomolar inhibitory activity, IC50 = 20 nM, and a high selectivity index, SI = 625. The Epc1 was determined for the most interesting compounds and no correlation with the trypanosomicidal effect was found. Therefore, an in silico study was carried out to obtain a pharmacophoric model and quantitative structure–trypanosomicidal activity relationship. The designed pharmacophore recognized the more potent and selective molecules, exhibiting five pharmacophoric features. A correlation coefficient R2 of 0.99 of pIC50 plotted against the predicted values indicated that the 3D-QSAR equation could be applied to further predictions of newly designed trypanosomicidal compounds.
1 Introduction
Chagas disease, caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi), is a neglected tropical endemic disease in Central and South America.1 As a result of international migrations, Chagas disease is also found now in non-endemic countries such as in the United States,2 Europe3 and Australia.4 In these countries where the vectors do not exist, the infection can be transmitted through the donation of infected blood or organs, and through vertical transmission from mother to child.5 The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that about 10 million people worldwide are currently infected, mainly in endemic areas of Latin America. This disease represents an important health problem in Central and South America and although mortality indexes have been decreased in the last few years, actually more than 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 deaths are estimated to occur annually from Chagas disease.6 This disease has two successive clinical phases: acute and chronic. There are two main drugs used for treatment: benznidazole and nifurtimox, developed more than 40 years ago, exhibit limited efficacy in the chronic phase and both present severe toxic side effects.7,8 The need for more effective drugs has stimulated the search for new compounds with potential clinical utility.
000 deaths are estimated to occur annually from Chagas disease.6 This disease has two successive clinical phases: acute and chronic. There are two main drugs used for treatment: benznidazole and nifurtimox, developed more than 40 years ago, exhibit limited efficacy in the chronic phase and both present severe toxic side effects.7,8 The need for more effective drugs has stimulated the search for new compounds with potential clinical utility.
In view of the structural diversity and wide range of pharmacological activities exhibited by compounds having a quinone scaffold, many natural and synthetic naphthoquinones have been tested against T. cruzi parasites as possible anti-Chagas agents.9,10 Thus, considering the important anti-trypanosomal and leishmanicidal activity exhibited by lapachol I (Fig. 1), Bolognesi and co-workers have synthesized a small library of 2-aryloxy-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives.11 The most active compound was 2-phenoxy-1,4-naphtoquinone II (Fig. 1), which showed an IC50 of 1.70 μM against the amastigote forms of T. cruzi, but with a low selectivity index (SI < 5).11
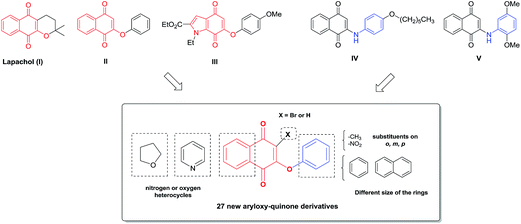 | ||
| Fig. 1 Chemical structures of lapachol, phenoxy- and phenylamino-quinones with trypanosomicidal activities and the designed template for new anti-T. cruzi agents. | ||
In the search for new compounds with improved trypanosomicidal activity, we have been focused on the synthesis of new aryloxy-indolequinones with different substitution patterns, which were tested for their trypanosomicidal effect and selectivity in cultures of T. cruzi epimastigotes and macrophages, respectively. Interestingly, 6-phenoxyindolequinone III (Fig. 1) displayed excellent nanomolar inhibitory activity, IC50 = 20 nM, and a high selectivity index, SI = 625.12 Based on these results, we recently carried out a study of 2-arylaminonaphthoquinone and 5H-benzo[b]carbazole-6,11-dione derivatives. These compounds were assayed against T. cruzi epi- and trypomastigotes and some of them against cancer cells and normal fibroblasts.13 It was found that certain chemical modifications on the naphthoquinone moiety increase the trypanosomicidal and cytotoxic effects. Several of these compounds were more potent than the reference drug nifurtimox against both stages of the parasite and exhibited increased selectivity against T. cruzi in comparison with VERO cells, being the most active 2-arylaminonaphthoquinone IV (Fig. 1). On the other hand, the 2-phenyl-aminonaphthoquinone V showed significant in vitro cytotoxicity against prostate and mammary cancer cells and high selectivity with respect to fibroblasts. A preliminary analysis confirmed an earlier conclusion that the replacement of a benzene ring by a pyridine ring condensed to the quinone core is an important modification to increase these activities.14,15 The attempts to disclose general structure–activity relationships using stereoelectronic and lipophilicity properties point out that the presence of a chlorine atom at C-3 and a highly lipophilic alkyl group or aromatic ring are newly observed elements with the aim of designing more selective cytotoxic and trypanosomicidal compounds.13
On the other hand, quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) studies have emerged as a useful tool to find relevant physicochemical descriptors for the design of new drugs,16,17 as well as to get some insight into the underlying mechanisms of action of the QSAR-based predicted activities. Recently, QSAR analysis was applied to naphthoquinone derivatives and can be useful in the search for new compounds with enhanced anti-trypanosomal activity.18–20
Herein, we designed a set of 27 new molecules based on the aryloxy-quinone scaffold (Fig. 1), which combine two pharmacophoric patterns of trypanosomicidal compounds (II–V). These new compounds could validate our hypothesis that chemical modifications on the naphthoquinone core or aromatic ring would increase the trypanosomicidal effects and the selectivity as well. The in vitro trypanosomicidal activity against T. cruzi epimastigotes and the selectivity index for the set of 27 compounds was evaluated. Additionally, considering that a possible mechanism of action is by reduction of the quinone system and the production of free-radical intermediates,15,21 the electrochemical properties for most active compounds were evaluated in order to find a probable correlation with their anti-T. cruzi activity. Furthermore, an in silico strategy was applied to obtain a pharmacophoric model and 3D-QSAR equation, to analyze the in vitro trypanosomicidal activity of the compounds under study.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Chemistry
A useful and direct approach for the synthesis of required aryloxy-quinones is through the nucleophilic substitution reaction of phenols with haloquinones in a basic medium at room temperature.11,22 As shown in Scheme 1, 2-aryloxy-naphthoquinones 3a–f (series I) were obtained in 40–97% through the reaction of phenols 2a–c with halonaphthoquinone 1a or 1b in dimethylformamide (DMF) in the presence of potassium carbonate. Similarly, reaction of halonaphthoquinone 1a or 1b with naphthols 2d,e afforded the corresponding naphthoquinones 3g–j in 53–95% yield.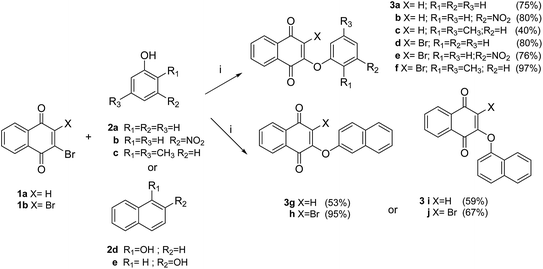 | ||
| Scheme 1 Synthesis of compounds of series I (3a–j). Reagents and conditions: (i) K2CO3, DMF, rt, 2–3 h. | ||
The compounds belonging to series II were synthesized starting from bromoquinolin-5,8-diones 6a and 6b (Scheme 2). These quinones were obtained by bromination (Br2/MeOH) of 8-hydroxyquinoline 4a or 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinoline 4b and subsequent oxidation of the corresponding dibromophenols 5a,b with nitric acid.23 The reaction of 6a and 6b with the phenols 2a–c or naphthols 2d,e furnished regiospecifically the corresponding 7-aryloxy-quinoline-5,8-dione derivatives 7a–i (24–92% yield).
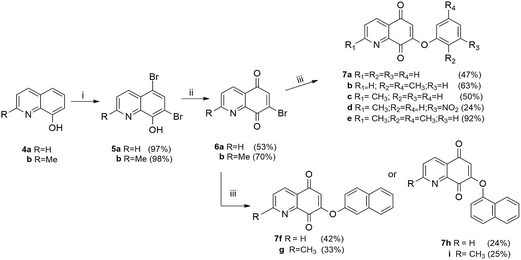 | ||
| Scheme 2 Synthesis of compounds of series II (7a–i). Reagents and conditions: (i) Br2, MeOH, rt, 5 min; (ii) HNO3, H2SO4, 0 °C, 30 min;23 (iii) K2CO3, 2a–e, DMF, rt, 3–5 h. | ||
The required bromobenzofuran-4,7-diones 10a,b (Scheme 3), were obtained using phenol 8 as the substrate. The bromination of 8 with two or four equivalents of Br2 in CHCl3, followed by oxidation with chromium trioxide, yielded the halobenzofuranquinones 10a,b.14 The reaction of 10a,b and the phenols 2a–e afforded compounds 11a–i (series III) in 23–83% yield. The chemical structures of the target compounds were established on the basis of their spectral properties (IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR and HRMS, see Experimental part and ESI†).
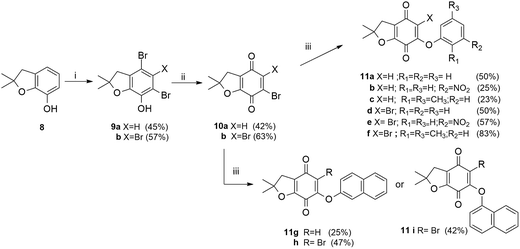 | ||
| Scheme 3 Synthesis of compounds of series III (11a–i). Reagents and conditions: (i) Br2, CHCl3, rt, 1.5 h; (ii) CrO3, H2O/AcOH, rt, 2 h; (iii) K2CO3, DMF, 2a–e, rt, 2 h. | ||
2.2 Trypanosomicidal effect
The in vitro trypanosomicidal activity of 2-aryloxy-naphthoquinones 3a–j (series I), 7-aryloxy-quinolinquinones 7a–i (series II) and 6-aryloxy-furonaphthoquinones 11a–i (series III), was initially tested against the epimastigote form of T. cruzi, Y strain (Tc II).24 For each derivative a dose–response assay, between 0.01 and 50 μM, was assayed to calculate the IC50 concentration (50% inhibitory concentration). Nifurtimox (Bayer) was used as the reference trypanosomicidal drug.25,26 All aryloxy-quinones exhibited a potent trypanosomicidal activity and they were more active than the reference drug nifurtimox, which had an IC50 of 7.0 μM (Table 1). Among them, compounds 3a–b, 7f and 7h displayed the most potent inhibitory activity with values of IC50 in the nanomolar order (IC50 < 90 nM for epimastigotes).| Entry | IC50a (μM) | J-774 IC50 (μM) | S.I.b | Epc1c (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a The results are the mean of three independent experiments.b Selectivity index: expressed as the ratio of IC50 in J-774 cells to IC50 in epimastigotes.c Values determined at c = 1 × 10−3 mol L−1, in DMF/TBAP, 0.1 mol L−1, ν = 50 mV s−1.d n.d.: not determined.e 5 μM was used for this assay. | ||||
| 3a | 0.05 ± 0.02 | <12.5 | <250 | −0.610 |
| 3b | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 12.5 | 625 | −0.526 |
| 3c | 0.17 ± 0.05 | <12.5 | <73.5 | −0.610 |
| 3d | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 18 | 163.6 | −0.397 |
| 3e | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 46 | 418.2 | −0.369 |
| 3f | 0.23 ± 0.06 | 39 | 169.6 | −0.397 |
| 3g | 0.15 ± 0.04 | <12.5 | <83.3 | −0.633 |
| 3h | 0.14 ± 0.05 | <12.5 | <89.3 | −0.456 |
| 3i | 0.17 ± 0.04 | <12.5 | <73.5 | −0.624 |
| 3j | 0.17 ± 0.06 | 19 | 111.8 | −0.440 |
| 7a | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 22 | 200 | −0.517 |
| 7b | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 18 | 163.6 | −0.555 |
| 7c | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 12.5 | 89.3 | −0.566 |
| 7d | 0.44 ± 0.09 | 12.5 | 28.4 | −0.515 |
| 7e | 0.23 ± 0.07 | <12.5 | <54.3 | −0.608 |
| 7f | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 15 | 375 | −0.508 |
| 7g | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 16 | 106.7 | −0.536 |
| 7h | 0.09 ± 0.04 | <12.5 | <138.9 | −0.517 |
| 7i | 0.17 ± 0.05 | <12.5 | <73.5 | −0.527 |
| 11a | 1.00 ± 0.02 | 21 | 21 | −0.550 |
| 11b | 2.30 ± 0.03 | 61 | 25.5 | −0.456 |
| 11c | 0.54 ± 0.13 | 44 | 81.5 | n.d.d |
| 11d | 5.00 ± 0.6 | 25 | 5.00 | −0.347 |
| 11e | 1.60 ± 0.2 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 11f | 1.80 ± 0.4 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 11g | 0.98 ± 0.17 | 21 | 21.4 | −0.508 |
| 11h | 7.00 ± 1.7 | ∼25 | ∼3.60 | −0.482 |
| 11i | 5.50 ± 0.4 | ∼25 | ∼4.54 | −0.465 |
| Nfxe | 7.00 ± 0.3 | 316 ± 0.5 | 40 | — |
2-Phenoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone 3a (IC50 = 50 nM) was selected as a reference compound to evaluate the effect of chemical modifications for compounds of series I. It was found that the incorporation of a withdrawing group in the aryloxy moiety (nitro derivative 3b) enhanced the trypanosomicidal effect and the compound with the highest activity (IC50 = 20 nM) was obtained. On the other hand, the electron donating methyl groups (3c) or α- and β-naphthyl rings (3g,i) weakly decreased the trypanosomicidal effect compared to 3a, but these compounds were still more active than nifurtimox (40 times). Regarding the replacement of the hydrogen atom at C-3 by bromine, compounds 3d–f showed a decrease in the trypanosomicidal effect compared with their un-halogenated analogs; whereas 2-naphthyloxyquinones 3h,j kept their anti-trypanosomal activity. Similar behavior was observed for the 2-phenylamino-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives previously studied.13
For the compounds belonging to series II (7a–i), the most active were 7f and 7h (IC50 = 40 and 90 nM, respectively). In this case, the presence of the α- or β-naphthyl ring bound to the quinone core increased the trypanosomicidal effect in comparison to the reference compound 7a (IC50 = 110 nM), in contrast to the results for series I. The nitro derivative 7d was the least active of this series, but still it was more potent than nifurtimox (16 fold). The presence of methyl substituents on the phenyl ring of 7a had no effect on the activity (7b). However, the trypanosomicidal activity of quinoline derivatives with a methyl group at C-2 was lower than their H-analogues, showing a decrease of up to four times (7f vs. 7g). Finally, analyzing the replacement of the benzene by a pyridine ring (series I vs. II), an increase in the trypanosomicidal effect was observed on the epimastigote form (except 3a vs. 7a). For instance, compound 7f is almost four times more potent than its carbocyclic analog 3g, with IC50 values of 40 nM and 150 nM, respectively. These results are in agreement with previous findings from our group that indicate the relevance of nitrogen substitution in the aromatic ring for activity of related compounds.13–15
The dihydrofurane derivatives of the series III (11a–i) were less active than the other series, with most IC50 values being >1.0 μM, except for compound 11c, which showed the lowest IC50 value (0.54 μM). These results suggest that the oxygen heterocyclic system fused to the quinone ring, decreasing the trypanosomicidal effect and that the halogen replacement at the quinone ring gives compounds with lower activity.
A preliminary analysis of several modifications on the naphthoquinone core showed a significant improvement in the trypanosomicidal activity in compounds bearing nitro group substitution (3b) and the replacement of a benzene ring by pyridine ring (7f and 7h), in comparison to the reference compound 3a.
2.3 Selectivity studies
Compounds with trypanosomicidal activity do not have pharmacological relevance when displaying high cytotoxicity on mammalian host cells and therefore exhibit low selectivity. For this reason, compounds with the highest trypanosomicidal effect were studied for their unspecific cytotoxicity on murine macrophages J-774 cells and the selective indexes (SI) were calculated as the ratio of the IC50 between epimastigotes and J-774 cells (Table 1). According to some authors searching for new strategies for the development of novel drugs for tropical disease, the selective index should be higher than 50.27,28 Table 1 shows the IC50 values for most compounds on J-774 cells and these results concluded that most of them (19 compounds) exhibited a better selectivity than nifurtimox (SI value = 40). Interestingly, compounds 3a, 3b, 3d, 3e, 3f, 3j, 7a, 7b, 7f, 7g and 7h included in series I and II showed a high selectivity index (SI values >100). Among them, compound 3b deserved special importance, because it exhibited the highest trypanosomicidal activity (IC50 value of 20 nM) and elevated selectivity in regard to its toxicity toward J-774 cells (SI value = 625). A second group of compounds (3c, 3g, 3h, 3i, 7c, 7e, 7i and 11c) was slightly more selective than nifurtimox (SI values among 70–90). Finally, a third group of compounds (11a, 11b, 11d, 11g, 11h, 11i and 7d) were less selective than nifurtimox (SI < 20) and most of them belonged to compounds of series III, which showed the lowest trypanosomicidal activity.A preliminary chemical structural analysis for the selectivity indicates that for those compounds of series I, the presence of the nitro group in the aryloxy moiety (3b and 3e) contributed to an increase in both the trypanosomicidal effect and the selectivity. The opposite effect was observed in the presence of dimethylphenyl (3c) or naphthyl groups (3g and 3i), that increased the toxicity in mammals and decreased the selectivity.
In previous studies, our group had reported that the substitution of hydrogen by halogen at C-2 in the quinone moiety increases the selectivity,13 nevertheless, for halogenated compounds (3d–f, 3h or 3j), there is no clear pattern. On the other hand, for those of series II (regarding 7a, SI = 200), the presence of the β-naphthyl group linked to the naphthoquinone provides access to more selective compounds (7f). In contrast, the replacement of the quinoline core by 2-methylquinoline in addition to the aryloxy substitution by dimethylphenyl or the α-naphthyl ring, significantly reduced the selectivity in all analogues.
There are several proposed mechanisms of action for the trypanosomicidal activity of quinone derivatives that could relate to the selectivity shown in this study. One of them is the well-known ability of quinones for generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) through a redox cycle with molecular oxygen and consequently strong oxidative stress and cell death.10,29–32 The biochemical differences between the parasite and host cells to avoid the damage mediated by ROS are considerable, meanwhile mammalian cells defend themselves efficiently against free radicals in diverse ways;33 T. cruzi’s defense mechanisms against oxidative stress are defective.34 On the other hand, it has been reported that quinones are inhibitors of trypanothione reductase (TR), an enzyme that constitutes part of the principal oxidative-stress defense of the T. cruzi35,36 and it is absent in the mammals. Studies on this issue are currently being developed in our laboratory.
2.4 Pharmacophore elucidation
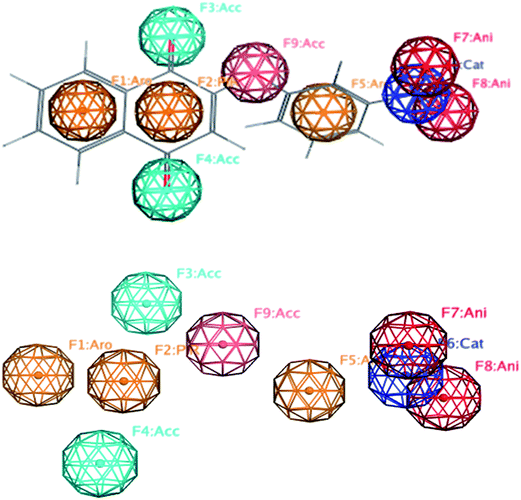
In order to generate a pharmacophore model (hypothesis), the compound with the highest trypanosomicidal activity (3b, IC50 20 nM) was chosen as a structural template. Once the tridimensional structure of the selected molecule 3b was created, the pharmacophore hypothesis was generated using the polar-charged-hydrophobic (PHC) scheme of MOE program.37 Several structural particularities were identified: a quinonic ring, aromatic rings, nitro group, and an oxygen bridge with the aromatic ring. Thus, using 3b as a template and with the PCH scheme, which combines polarity, charge and hydrophobicity, different pharmacophoric features centered in the middle of the atomic sets (centroids), with aromaticity (Aro), rings with π delocalization (Pir), positive charge (Cat), negative charge (Ani), and hydrogen acceptor capacity (Acc) were defined (Fig. 2).Once the five pharmacophoric features of 3b were identified, a combination of them, selecting as essential aromatic (Aro) and hydrogen acceptor (Acc) (Fig. 3) and taking any four of them at a time, a search algorithm was found to obtain just the molecules with selectivity index greater than 100. By this mean, a search was made over the quinone databases and all eleven selective molecules were found as hits: 3b, 3e, 7f, 7a, 3f, 7b, 3d, 3j, 3h, 7c and 7d. From them, all the selective molecules except one (7g) were detected, having 89% recovery of true positives. Three molecules (3h, 7c and 7d) are false positives, this is they are non-selective, being detected by the pharmacophore as positives. To have a quantitative measurement of this result, it is useful to calculate the enrichment factor R (eqn (1)).
| R = [number of selective hits (=8)/number of non-selective hits (=17)]/[number of all selective (=9)/number of all non-selective (=19)] = 0.99 | (1) |
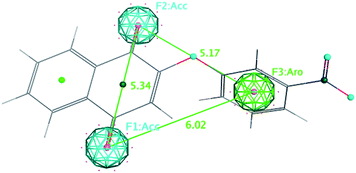 | ||
| Fig. 3 Selective pharmacophore features and interatomic distances between the essential features Acc (F1 and F2) and Aro (F3). | ||
2.5 Electrochemical study
The cytotoxicity of quinones has been mainly attributed to two processes; redox cycling that generates ROS or electrophilic arylation of critical cellular nucleophiles, in both cases the single-electro-reduction of the quinone ring is the first step. Accordingly, several attempts to establish some correlation between the biological activity and redox potentials of quinones have been reported.38–41 Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is commonly used to obtain electrochemical parameters for biological studies with quinones, such as potentials of the oxidation (Epa) and reduction (Epc) peaks or Eredox (for reversible systems).38–43 Therefore, redox properties for the most active compounds of each series were determined by CV in a typical measurement.Fig. 4 shows the cyclic voltammograms for the most active compounds of each series (for the other compounds, CV profiles are available in the ESI†). All quinones exhibited quasi-reversible reduction behavior, which is a typical quinone/semiquinone/hydroquinone triad in equilibrium, and the overall CV profiles are similar to those reported for other quinones.38,39,44,45
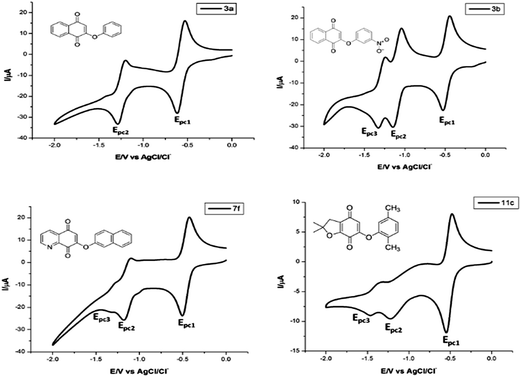 | ||
| Fig. 4 Cyclic voltammograms of quinones 3a, 3b, 7f and 11c (1.0 mM). DMF/TBAP (0.1 M), glassy carbon electrode, cathodic direction, scan rate 50 mV s−1. | ||
The Epc1 values were obtained from the CV profile of each compound (Table 1), which is most commonly used to compare biological activities. For compounds from series I, the relative reduction potential is as follows: 3e > 3d ∼ 3f > 3j > 3h > 3b > 3a ∼ 3c > 3i > 3g. An interesting characteristic that presents the five compounds that are most easily reduced is the presence of the bromine direct attachment of the quinone core, which is according to the electron-withdrawing feature of this halogen. The reduction trend for compounds of series II was 7f > 7d > 7a ∼ 7h > 7i > 7g > 7b > 7c > 7e. The values for the Epc1 for these compounds were around −0.50 V, which is a smaller value than those with a halogen of series I and confirms the effect of this substituent. However, the replacement of the benzene ring by the pyridine ring facilitates the electron transfer due to the nitrogen atom attached to the quinone moiety. On the other hand, the presence of an electron-donating methyl group (in either aromatic ring), increased the barrier to reduction (7i, 7g, 7b, 7c and 7e) except for 7d, which could be related to the presence of the nitro group in the meta-position of the phenyl moiety. The ease of reduction in series III, expressed by Epc1 (Table 1) was 11d > 11b > 11i > 11h > 11g > 11a. All of them display behavior similar to that observed for other benzofuranquinones. The first four compounds of this series shares the presence of a bromine or nitro group as a substituent, which confirms the role of these substituents in the reduction process, diminishing the values of the Epc1.
However, attempts to reveal an eventual structure–activity relationship using values of Epc1 and pIC50 were unsuccessful for each series (Fig. 5). The lack of correlation between these parameters could indicate that the first reduction potential of these aryloxy-quinones is not decisive in the trypanosomicidal activity or, although essential for a cellular event, does not always show a quantitative correlation with this property.39 In fact, many other factors such as lipophilicity, membrane permeability, etc., need critical consideration in order to rationalize the relationship of structural pattern and trypanosomicidal activity. Considering the small correlation between Epc1 and pIC50, other tools to understand the trypanosomicidal activity were explored. With this goal in mind, we performed the generation of 3D-QSAR models to correlate chemical structures of quinones with their biological data to identify specific features that influence the observed trypanosomicidal properties.46–49
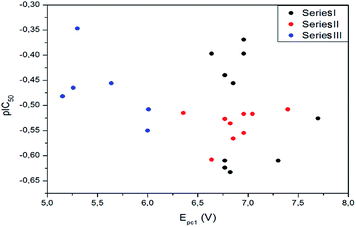 | ||
| Fig. 5 Graphs correlating the values of Epc1 of series I, II and III of quinones with the trypanosomicidal effect, represented by pIC50. | ||
2.6 3D-QSAR
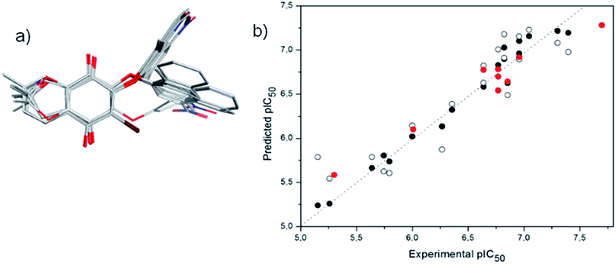
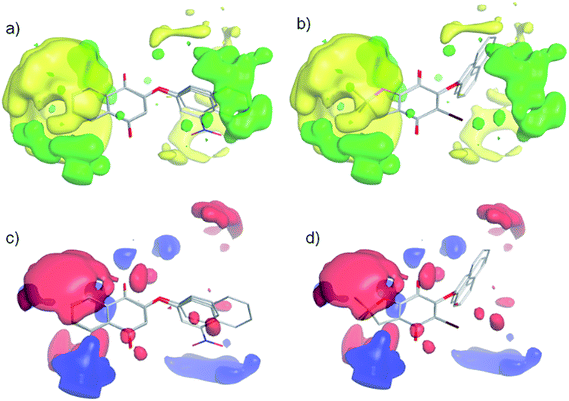
A 3D-QSAR-correlation analysis was performed with a set of 28 aryloxy-quinones with potent trypanosomicidal activity, selecting 19 and 9 compounds as the training and test sets, respectively. Conformational sampling on each molecule by quenched molecular dynamics and alignment by an atom-based fashion was carried out using Open3DAlign. Then, derivation of 3D-QSAR models was carried out by Partial Least-Squares (PLS) analysis with Iterative Variable Elimination (IVE-PLS) procedure by means of Open3DQSAR.49 The statistical results for 3D-QSAR modelling gave internal cross-validation qLMO2 of 0.75 and qLOO2 of 0.78, with five components in all models. Fig. 6a shows the aligned molecules and Fig. 6b the correlations between experimental versus predicted values of pIC50. The correlation coefficient of our model was R2 = 0.99, and the standard deviation of the error of prediction (SDEP) of 0.324 for training set, as well as R(pred)2 = 0.94 and SDEP of 0.115 for the test set. These data indicate that a significant 3D-QSAR model was obtained.For the 3D-QSAR modeling, the contour maps were created using the data from PLS analyses. These maps help us to explain the structural features of the compounds that contribute towards the anti-trypanosomicidal activity of the aryloxy-quinones. The steric contour map indicates the areas where the bulky substituents are predicted to increase (green) or decrease (yellow) the activity (Fig. 7a and b). Therefore, considering the yellow area around the aromatic moiety suggests that this ring should not have bulky groups. Furthermore, in compounds with a 2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran system and a bromine atom at the quinone ring (11d, 11e, 11h and 11i), the halogen substituent shifts the aryloxy group, inducing an unfavorable interaction, and consequently decreases the biological activity (Fig. 7b). The electrostatic map shows a red contour where high electron density (negative charge) would increase the activity, and the blue contour displays areas where low electron density (partial positive charge) is expected to increase the activity (Fig. 7c and d). The quinone ring is thought to be critical for the biological activity and the changes in its electron density might have caused an incremental increase in activity. The most active compound 3b received the influence of the NO2 electron-withdrawing group, having a positive delocalized polar region in the NO2 substituted aromatic ring. According to that, the electrostatic contour map (Fig. 7c) of the aromatic ring in 3b has a positive-charge favored region. The electrostatic contour maps indicated the positive electrostatic interaction of the aromatic ring with a possible receptor, which could increase the activity. In comparison, this interaction is lost in the less active compound 11i (Fig. 7d).
3 Conclusions
We have synthesized 27 new aryloxyquinones considering the 2-phenoxy-naphthoquinone (3a) as a reference compound and were grouped in three series according to similar structural patterns: 2-aryloxy-naphthoquinones 3a–j, 7-aryloxy-quinolinquinones 7a–i and 6-aryloxy-furonaphthoquinones 11a–i. All compounds were evaluated as trypanosomicidal agents and tested for their unspecific cytotoxicity on murine macrophages J-774 cells. Most of these compounds were more potent than the reference drug nifurtimox vs. epimastigote form and exhibited unprecedented selectivity against T. cruzi in comparison with J-774 cells, notably the 2-(3-nitrophenyloxy)-naphthoquinone 3b (IC50 = 20 nM and SI = 625). Also, it was demonstrated that certain chemical modifications on the naphthoquinone moiety and on the aryloxy group significantly increased the trypanosomicidal effect and the selectivity of some derivatives. Electrochemical studies were carried out in order to find out a possible structure–activity relationship and used in an attempt to understand this biological activity, but no correlation was found between the Epc1 and the pIC50. Because of that, in silico studies were done through pharmacophoric mapping and QSAR analyses. Eight out of nine molecules with the best IC50 and SI values were chosen using the selective designed pharmacophore, proving that this procedure is able to find active and selective molecules with an enrichment factor of R = 0.99. A 3D-QSAR equation was obtained with a coefficient of determination R2 of 0.99 and the contour maps indicated that the trypanosomicidal activity was related to the steric and electronic features in the aryloxy moiety or ring fused to the quinone system. Our current work is focused on understanding in depth the selectivity and mechanism of action of the most promising compounds.4 Experimental
4.1 Materials and measurements
Melting points were determined on a Kofler Thermogerate apparatus and were uncorrected. Infrared spectra were recorded on a JASCO FT/IR-400 spectrophotometer. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectra were recorded, unless otherwise specified, on a Bruker AM-400 instrument using deuterochloroform solutions containing tetramethylsilane as an internal standard. Mass spectra were obtained on a HP 5988A mass spectrometer. HRMS-ESI-MS experiments were carried out using a Thermo Scientific Exactive Plus Orbitrap spectrometer with a constant nebulizer temperature of 250 °C. The experiments were carried out in positive ion mode, with a scan range of m/z 300.00–1510.40 with a resolution of 140.000. The samples were infused directly into the ESI source, via a syringe pump, at flow rates of 5 μL min−1, through the instrument’s injection valve. Thin layer chromatography (tlc) was performed using Merck GF-254 type 60 silica gel. Column chromatography was carried out using Merck type 9385 silica gel. The purity of the compounds was determined by tlc and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS).4.2 Synthesis
2-Phenoxynaphthalene-1,4-dione (3a). Yellow solid, yield 75%, mp 102–103 °C (lit.11 101 °C). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 5.99 (s, 1H), 7.15 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.34 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.46 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.74–7.81 (m, 2H), 8.04–8.10 (m, 1H), 8.18–8.23 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 113.34, 121.07 (2C), 126.18, 126.60, 126.73, 130.40 (2C), 131.06, 131.91, 133.50, 134.41, 152.67, 160.45, 179.86, 184.88. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1613, 1672, 1591. HRMS-ESI for (C16H11O3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 251.0708. Found: 251.0699.
2-(3-Nitrophenoxy)naphthalene-1,4-dione (3b). Yellow solid, yield 80%, mp 170–173 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 6.05 (s, 1H), 7.53 (dd, J = 1.5, 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.69 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.74–7.85 (m, 2H), 8.00–8.12 (m, 2H), 8.16–8.25 (m, 2H).13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 115.14, 116.53, 121.43, 126.53, 127.03, 127.23, 131.05, 131.34, 131.90, 134.00, 134.83, 149.54, 153.61, 159.31, 179.36, 184.53. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1620, 1654, 1528, 1472, 1178, 1032. HRMS-ESI for (C16H9NO5 [M + H]+). Calcd: 296.0559. Found: 296.0560.
2-(2,5-Dimethylphenoxy)naphthalene-1,4-dione (3c). Yellow oil, yield 63%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 2.15 (s, 3H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 5.83 (s, 1H), 6.86 (s, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.74–7.78 (m, 2H), 8.02–8.09 (m, 1H), 8.20 (dd, J = 6.1, 2.7 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 15.38, 20.98, 112.86, 121.62, 126.28, 126.67, 126.82, 127.62, 131.27, 131.80, 132.12, 133.54, 134.47, 138.07, 150.74, 159.85, 179.94, 185.14. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1610, 1651, 1288, 1258, 1222. HRMS-ESI for (C18H14O3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 279.1021. Found: 279.1032.
2-Bromo-3-phenoxynaphthalene-1,4-dione (3d). Yellow solid, yield 80%, mp 160–162 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 7.01 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.13 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.29–7.38 (m, 2H), 7.71–7.81 (m, 2H), 7.98–8.06 (m, 1H), 8.16–8.23 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 116.69, 124.10, 127.35, 127.69, 129.88, 130.73, 131.17, 134.42, 134.56, 156.06, 156.41, 177.47, 178.48. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1613, 1672, 1206, 1245, 1159, 1021. HRMS-ESI for (C16H9BrO3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 327.9735. Found: 329.1719.
2-Bromo-3-(3-nitrophenoxy)naphthalene-1,4-dione (3e). Yellow solid, yield 76%, mp 197–199 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 7.40 (ddd, J = 0.8, 2.5, 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.76–7.86 (m, 3H), 8.00–8.10 (m, 2H), 8.23–8.27 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 111.93, 118.78, 122.78, 127.24, 127.75, 128.72, 130.28, 130.63, 131.28, 134.36, 134.59, 149.49, 155.25, 156.52, 176.92, 177.76. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1677, 1536, 1349, 1245, 1018. HRMS-ESI for (C16H9BrNO5 [M + H]+). Calcd: 373.9664. Found: 373.9648.
2-Bromo-3-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)naphthalene-1,4-dione (3f). Orange solid, yield 97%, mp 196–198 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 2.22 (s, 3H), 2.38 (s, 3H), 6.48 (s, 1H), 6.86 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.15 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.68–7.81 (m, 2H), 7.98–8.09 (m, 1H), 8.18–8.27 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 15.79, 20.90, 115.94, 124.68, 124.95, 125.11, 126.75, 127.26, 127.55, 128.21, 131.30, 134.25, 134.43, 136.83, 154.82, 156.76, 177.54, 178.51. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1679, 199, 1244, 1098, 1002. HRMS-ESI for (C18H13BrO3 [M + Na+]+). Calcd: 380.9925. Found: 381.2984.
2-(Naphthalen-2-yloxy)naphthalene-1,4-dione (3g). Yellow solid, yield 95%, mp 163–164 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 6.01 (s, 1H), 7.27 (dd, J = 2.4, 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.48–7.57 (m, 2H), 7.60 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.75 (dd, J = 2.8, 5.5 Hz, 2H), 7.80–7.84 (m, 1H), 7.87–7.90 (m, 1H), 7.94 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 8.02–8.07 (m, 1H), 8.18–8.22 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 113.73, 118.35, 120.11, 126.28, 126.37, 126.84, 127.18, 127.72, 128.02, 130.80, 131.18, 131.74, 132.03, 133.58, 134.07, 134.49, 150.29, 160.58, 179.95, 184.90. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1629, 1671, 1242. HRMS-ESI for (C20H12O3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 301.0865. Found: 301.0865.
2-Bromo-3-(naphthalene-2-yloxy)naphthalene-1,4-dione (3h). Orange solid, yield 67%, mp 166–168 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 7.27–7.22 (m, 1H), 7.33 (dd, J = 8.9, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (m, 2H), 7.67 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.74 (m, 2H), 7.81 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 8.01 (dd, J = 7.4, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 8.24–8.20 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 111.78, 117.98, 125.13, 126.91, 127.19, 127.35, 127.69, 127.89, 128.01, 130.21, 130.49, 130.67, 131.16, 133.92, 134.40, 134.54, 154.15, 156.16, 177.39, 178.49. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1671, 1509, 1572, 1195, 1158. HRMS-ESI for (C20H11BrO3 [M + Na+]+). Calcd: 400.9789. Found: 400.9766.
2-(Naphthalen-1-yloxy)naphthalene-1,4-dione (3i). Yellow solid, yield 53%, mp 156–158 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 5.82 (s, 1H), 7.27 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.45–7.59 (m, 3H), 7.71–7.79 (m, 2H), 7.81 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.86 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.92 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.03 (br, 1H), 8.24 (br, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 113.78, 117.63, 121.24, 125.75, 126.05, 126.33, 126.89, 126.93, 127.12, 127.16, 128.36, 131.27, 132.10, 133.64, 134.53, 135.21, 148.64, 160.62, 179.91, 185.00. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1602, 1682, 1034, 1248. HRMS-ESI for (C20H12O3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 301.0865. Found: 301.0859.
2-Bromo-3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)naphthalene-1,4-dione (3j). Red solid, yield 59%, mp 161–163 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 6.74 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.25 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.52–7.65 (m, 3H), 7.67–7.79 (m, 2H), 7.86 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H), 7.97 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.20 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 8.34 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 109.60, 121.99 (2C), 124.15, 125.22, 126.48, 127.09, 127.37, 127.72, 127.81, 130.72 (2C), 131.21, 134.43, 134.57, 134.97, 152.56, 156.74, 177.27, 178.51. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1682, 1601, 1570, 1247, 1221. HRMS-ESI for (C20H11BrO3 [M + Na+]+). Calcd: 400.9789. Found: 400.9771.
7-Phenoxyquinoline-5,8-dione (7a). Yellow solid, yield 47%, mp 172–173 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 6.04 (s, 1H), 7.19–7.13 (m, 2H), 7.34 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.49 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (dd, J = 4.7, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 8.41 (dd, J = 1.7, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 9.07 (dd, J = 1.7, 4.7 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 112.78, 115.50, 121.08, 126.95, 128.18, 129.06, 129.61, 130.58, 134.46, 147.00, 152.52, 154.55, 161.10, 178.05, 183.73. IR (KBr, cm−1): 3052, 3016, 1610, 1280, 1240, 1083. HRMS-ESI for (C15H9NO3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 252.0661. Found: 252.0654.
7-(2,5-Dimethylphenoxy)quinoline-5,8-dione (7b). Orange solid, yield 63%, mp 177–179 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 2.16 (s, 3H), 2.35 (s, 3H), 5.91 (s, 1H), 6.87 (s, 1H), 7.04 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.72 (dd, J = 4.7, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 8.41 (dd, J = 1.7, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 9.07 (dd, J = 1.7, 4.7 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 183.84, 178.01, 160.37, 154.47, 150.52, 147.04, 138.18, 134.44, 131.86, 129.10, 128.15, 127.83, 126.53, 121.45, 112.26, 20.95, 15.34. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1654, 1613, 1244, 1141. HRMS-ESI for (C17H13NO3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 280.0974. Found: 280.0968.
2-Methyl-7-phenoxyquinoline-5,8-dione (7c). Yellow solid, yield 49%, mp 165–167. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 2.80 (s, 3H), 5.98 (s, 1H), 7.15 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.32 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.55 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.27 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 25.60, 112.88, 121.49 (2C), 127.17, 127.27, 128.44, 130.84 (2C), 134.85, 146.88, 152.98, 161.27, 165.21, 178.63, 184.27. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1640, 1614, 1582, 1289, 1226. HRMS-ESI for (C16H11NO3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 266.0817. Found: 266.0810.
2-Methyl-7-(3-nitrophenoxy)quinoline-5,8-dione (7d). Yellow solid, yield 24%, mp 197–198 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 2.81 (s, 3H), 6.06 (s, 1H), 7.54 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.70 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 8.05 (s, 1H), 8.22 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 8.29 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 183.52, 177.72, 165.38, 159.71, 153.38, 149.56, 146.44, 134.71, 131.44, 128.41, 127.36, 126.94, 121.66, 116.65, 114.06, 25.37. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1698, 1654, 1350, 1258, 1163. HRMS-ESI for (C16H10N2O5 [M + H]+). Calcd: 311.0668. Found: 311.0663.
7-(2,5-Dimethylphenoxy)-2-methylquinoline-5,8-dione (7e). Yellow solid, yield 92%, mp 165–166 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 2.15 (s, 3H), 2.34 (s, 3H), 2.80 (s, 3H), 5.85 (s, 1H), 6.86 (s, 1H), 7.03 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.27 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 15.28, 20.90, 25.20, 111.95, 121.49, 126.51, 126.92, 127.68, 128.05, 131.77, 134.47, 138.05, 146.53, 150.57, 160.11, 164.74, 178.21, 183.98. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1652, 1322, 1114, 1110. HRMS-ESI for (C18H15NO3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 294.1130. Found: 294.1121.
7-(Naphthalen-2-yloxy)quinoline-5,8-dione (7f). Yellow solid, yield 42%, mp 190–191 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 6.07 (s, 1H), 7.27 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (m, 2H), 7.61 (s, 1H), 7.71 (dd, J = 5.1, 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.79–7.93 (m, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 8.39 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 9.07 (d, J = 3.7 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 113.03, 118.43, 119.92, 126.54, 127.31, 127.77, 128.06, 128.18, 129.07, 130.96, 131.84, 134.04, 134.45, 147.02, 150.02, 154.57, 161.16, 178.09, 183.67. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1649, 1222, 1003. HRMS-ESI for (C19H11NO3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 301.0739. Found: 302.0809.
2-Methyl-7-(naphthalen-2-yloxy)quinoline-5,8-dione (7g). Yellow solid, yield 33%, mp 198–199 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 2.80 (s, 3H), 6.01 (s, 1H), 7.24–7.30 (m, 1H), 7.49–7.58 (m, 3H), 7.60 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.79–7.91 (m, 2H), 7.93 (t, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 8.25 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 25.25, 112.76, 118.43, 120.02, 126.44, 126.92, 127.22, 127.72, 128.01, 128.11, 130.84, 131.77, 134.01, 134.49, 146.52, 150.11, 160.95, 164.85, 178.27, 183.83. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1696, 1586, 1283, 1176. HRMS-ESI for (C20H13NO3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 316.0974. Found: 316.0964.
7-(Naphthalen-1-yloxy)quinoline-5,8-dione (7h). Yellow solid, yield 24%, mp 118–120 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 6.07 (s, 1H), 7.27 (dd, J = 1.6, 8.9 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (m, 2H), 7.61 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (dd, J = 4.7, 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.81–7.85 (m, 1H), 7.88–7.92 (m, 1H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 8.39 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 9.07 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 113.01, 118.43, 119.92, 126.54, 127.31, 127.76, 128.05, 128.19, 129.06, 130.96, 131.83, 134.03, 134.45, 147.01, 149.99, 154.57, 161.16, 178.09, 183.67. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1656, 1609, 1242. HRMS-ESI for (C19H11NO3 [M]−). Calcd: 300.0666. Found: 300.0656.
2-Methyl-7-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)quinoline-5,8-dione (7i). Yellow solid, yield 25%, mp 199–200 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 2.18 (s, 3H), 6.43 (s, 1H), 6.82 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.69–7.75 (m, 3H), 7.98 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 8.14–8.18 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 15.79, 115.93, 124.68, 124.94, 126.72, 127.26, 127.55, 128.21, 130.65, 131.16, 131.29, 134.22, 134.40, 134.51, 136.79, 142.58, 154.81, 156.76, 177.54, 178.56. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1653, 1615, 1225. HRMS-ESI for (C20H13NO3 [M]−). Calcd: 314.0823. Found: 314.0814.
2,2-Dimethyl-6-phenoxy-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4,7-dione (11a). Orange oil, yield 47%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 1.56 (s, 6H), 2.92 (s, 2H), 5.47 (s, 1H), 7.08 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.44 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 28.44 (2C), 39.63, 93.44, 107.71, 117.94, 121.06 (2C), 126.79, 130.45 (2C), 153.02, 158.61, 161.13, 178.42, 180.24. IR (KBr, cm−1): 2923, 1653, 1249, 1207. HRMS-ESI for (C16H14O4 [M + H]+). Calcd: 271.0970. Found: 271.0978.
2,2-Dimethyl-6-(3-nitrophenoxy)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4,7-dione (11b). Orange-red oil, yield 26%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 1.58 (s, 6H), 2.94 (s, 2H), 5.55 (s, 1H), 7.48 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (s, 1H), 8.18 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 28.34 (2C), 39.46, 93.70, 109.18, 116.43, 118.32, 121.42, 127.15, 131.26, 149.41, 153.65, 158.44, 159.65, 177.53, 179.55. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1613, 1535, 1203. HRMS-ESI for (C16H13NO6 [M + H]+). Calcd: 316.0821. Found: 316.0792.
6-(2,5-Dimethylphenoxy)-2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4,7-dione (11c). Orange-red oil, yield 50%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 1.57 (s, 6H), 2.13 (s, 3H), 2.31 (s, 3H), 2.92 (s, 2H), 5.34 (s, 5H), 6.79 (s, 1H), 6.99 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.14 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 15.25, 20.85, 28.31 (2C), 39.47, 93.25, 107.03, 117.76, 121.31, 126.34, 127.52, 131.63, 137.88, 150.91, 158.51, 160.28, 178.24, 180.21. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1659, 1589, 1104. HRMS-ESI for (C18H18O4 [M + H]+). Calcd: 299.1283. Found: 299.1273.
5-Bromo-2,2-dimethyl-6-phenoxy-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4,7-dione (11d). Red solid, yield 50% mp 140–142 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 1.56 (s, 6H), 2.84 (s, 2H), 6.97 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.12 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.28–7.36 (m, 2H), 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 28.45 (2C), 39.5, 93.95, 116.85 (2C), 118.85, 120.31, 124.14, 129.90 (2C), 155.11, 156.66, 157.54, 173.37, 176.15. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1653, 1588, 1282. HRMS-ESI for (C16H13BrO4 [M]). Calcd: 347.9997. Found: 348.0137.
5-Bromo-2,2-dimethyl-6-(3-nitrophenoxy)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4,7-dione (11e). Red solid, yield 57%, mp 177–179 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 1.58 (s, 6H), 2.87 (s, 2H), 7.36 (ddd, J = 0.9, 2.5, 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.52 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.76 (t, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (ddd, J = 0.9, 2.1, 8.2 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 28.46 (2C), 39.50, 94.34, 111.84, 118.98, 119.04, 121.38, 123.24, 130.63, 149.26, 154.06, 156.75, 157.73, 172.82, 175.57. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1693, 1647, 1577, 1552, 1268, 1243. HRMS-ESI for (C16H12BrNO6 [M + H]+). Calcd: 393.9926. Found: 393.9908.
5-Bromo-6-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)-2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4,7-dione (11f). Orange solid, yield 83%, mp 146–147 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 1.56 (s, 6H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 2.84 (s, 2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.84 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 15.84, 21.24, 28.31, 39.53, 93.74, 116.31, 118.51, 119.06, 121.41, 124.81, 125.05, 131.34, 136.84, 155.13, 155.73, 157.48, 173.41, 176.23. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1674, 1656, 1570, 1207. HRMS-ESI for (C18H17BrO4 [M + H]+). Calcd: 377.0388. Found: 379.0361.
2,2-Dimethyl-6-(naphthalen-2-yloxy)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4,7-dione (11g). Orange-red oil, yield 25%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 1.56 (s, 6H), 2.94 (s, 2H), 5.51 (s, 1H), 7.20 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 7.52 (dd, J = 4.1, 7.4 Hz, 3H), 7.80 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.86 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H) 7.91 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 28.41 (2C), 39.61, 93.43, 107.98, 117.96, 118.28, 119.99, 126.44, 127.23, 127.74, 128.04, 130.75, 131.77, 134.02, 150.51, 158.62, 161.11, 178.39, 180.13. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1672, 1594, 1197. HRMS-ESI for (C20H16O4 [M + H]+). Calcd: 321.1127. Found: 321.1127.
5-Bromo-2,2-dimethyl-6-(naphthalene-2-yloxy)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4,7-dione (11h). Red solid, yield 47%, mp 182–183 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 1.63 (s, 6H), 3.01 (s, 2H), 7.62 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 3H), 7.71 (t, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.85–7.97 (m, 2H), 9.50 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 28.56 (2C), 40.20, 93.10, 112.51, 119.63, 121.31, 125.92, 126.80, 127.95, 128.09, 128.20, 129.08, 131.59, 132.05, 150.68, 156.04, 156.92, 169.03, 180.24. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1681, 1647, 1341. HRMS-ESI for (C20H15BrO4 [M + H]+). Calcd: 399.0232. Found: 399.2946.
5-Bromo-2,2-dimethyl-6-(naphthalene-1-yloxy)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4,7-dione (11i). Orange solid, yield 42%, mp 179–180 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 1.61 (s, 6H), 2.98 (s, 2H), 7.26 (br, 1H), 7.61–7.71 (m, 2H), 7.81 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.96 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.11 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 8.43 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 28.40, 39.64, 93.06, 119.26, 119.60, 121.07, 121.15, 127.29 (2C), 127.59 (2C), 127.94 (2C), 128.70 (2C), 133.73, 157.87, 168.96, 178.49, 180.85. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1793, 1650, 1370. HRMS-ESI for (C20H15BrO4 [M + H]+). Calcd: 399.0232. Found: 399.1966.
4,5,6-Tribromo-2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-ol (9b). To a solution of 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranol (1 mmol) in chloroform (30 mL), under magnetic stirring at room temperature, was added dropwise a solution of bromine (5 mmol) in chloroform (15 mL). The mixture was stirred for 1.5 hour and then was washed with sodium thiosulfate solution (3 × 15 mL) and water (3 × 15 mL). The organic extract was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated. The crude was purified on silica gel column using dichloromethane as eluent. White solid, yield 57%, mp 120–121 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 1.53 (s, 6H), 3.07 (s, 1H), 5.43 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 28.40 (2C), 46.46, 89.51, 112.40, 112.85, 116.10, 130.07, 138.14, 145.10.
5,6-Dibromo-2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4,7-dione (10b). A solution of chromium oxide (2 mmol) in water (4 mL) was added dropwise at room temperature to a solution containing the compound 9b (0.5 mmol) in 9 mL of a mixture of glacial acetic acid/water (3.5/1). The mixture was stirred for two hours and then water (20 mL) was added and extracted with CH2Cl2. The organic phase was washed with sodium bicarbonate solution 10% until neutral, dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated. The crude product was purified on a silica gel column using dichloromethane as the eluent. Red solid, yield 63%, mp 108–110 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 1.57 (s, 6H), 2.94 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 28.23, 40.09, 46.47, 93.76, 120.27, 135.25, 141.46, 156.97, 170.58, 174.36. IR (KBr, cm−1): 1639, 1684, 1177, 762. HRMS-ESI for (C10H8Br2O3 [M + H]+). Calcd: 334.8918. Found: 336.8887.
4.3 Biology
T. cruzi Y strain epimastigotes were grown at 28 °C in an axenic medium (BHI-tryptose) as previously described,25,26 complemented with 5% foetal bovine serum. Epimastigotes from a 10 day-old culture (stationary phase) were inoculated into 50 mL of fresh culture medium to reach an initial concentration of 1 × 106 cells per mL. Cell growth was monitored by measuring the absorbance of the culture at 600 nm every day. Before inoculation, the media was supplemented with a given amount of the drug from a stock solution in DMSO (25 mM). The final DMSO concentration in the culture medium never exceeded 0.4%, and the control was run in the presence of 0.4% DMSO and in the absence of drugs. The percentage of inhibition (% GI) and IC50 values, 50% inhibitory concentrations, and parasite growth was followed in the absence (control) and in the presence of a range of concentrations of the corresponding drug. On day 5, the absorbance of the culture was measured and related to the control. The IC50 value was taken as the concentration of drug needed to reduce the absorbance ratio to 50%.25,26 J-774 murine macrophage-like cells (ATCC, USA) were maintained by passage in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) containing 4 mM L-glutamine, and supplemented with 10% heat inactivated foetal calf serum and 1% of antibiotics (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 U mL−1 penicillin and 10
000 U mL−1 penicillin and 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 U mL−1 streptomycin). J-774 cells were seeded (1 × 105 cells per well) in 96 well microplates with 200 mL of RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 20% heat-inactivated foetal calf serum. Cells were allowed to attach for 48 h in a humidified 5% CO2/95% air atmosphere at 37 °C and then exposed to compounds (100.0 to 400.0 μM) for 48 h. Afterwards, cell viability was assessed by measuring the mitochondrial-dependent reduction of MTT (Sigma) to formazan. For that purpose, MTT was added to cells to a final concentration 0.4 mg mL−1 and cells were incubated at 37 °C for 3 h. After removing the media, formazan crystals were dissolved in DMSO (0.18 mL), and the absorbance at 595 nm was read using a microplate spectrophotometer. Results are expressed as IC50 (compound concentration that reduce 50% control absorbance at 595 nm).25 Every IC50 is the average of three independent experiments. The selectivity index, SI, was expressed as the ratio between IC50 in macrophages and IC50 in T. cruzi (Y strain).
000 U mL−1 streptomycin). J-774 cells were seeded (1 × 105 cells per well) in 96 well microplates with 200 mL of RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 20% heat-inactivated foetal calf serum. Cells were allowed to attach for 48 h in a humidified 5% CO2/95% air atmosphere at 37 °C and then exposed to compounds (100.0 to 400.0 μM) for 48 h. Afterwards, cell viability was assessed by measuring the mitochondrial-dependent reduction of MTT (Sigma) to formazan. For that purpose, MTT was added to cells to a final concentration 0.4 mg mL−1 and cells were incubated at 37 °C for 3 h. After removing the media, formazan crystals were dissolved in DMSO (0.18 mL), and the absorbance at 595 nm was read using a microplate spectrophotometer. Results are expressed as IC50 (compound concentration that reduce 50% control absorbance at 595 nm).25 Every IC50 is the average of three independent experiments. The selectivity index, SI, was expressed as the ratio between IC50 in macrophages and IC50 in T. cruzi (Y strain).
4.4 Pharmacophore
The 3D-structure of the pharmacophore hypothesis was carried out using “Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) software version 2013–2014”, Chemical Computing Group INC., 1010 Sherbrook Street West, Suite 910, Montreal, H3A 2R7, Canada.4.5 3D-QSAR
The data set was split into 19 compounds as the training set (2/3 of the compounds) and 9 compounds as the test set (1/3 of the compounds). Alignments were carried out atom-by-atom based on a conformational sampling by quenched molecular dynamics, carried out using Open3Daling50 on each structure (MMFF94 force-field, GB/SA implicit solvent model, 1000 5 ps molecular dynamics runs at 1000 K followed by energy minimization), keeping the most stable conformations in a 8 kcal mol−1 range from the global minimum; this energy strain threshold was previously shown to include a percentage of experimentally found bioactive compounds. The aligned ligand ensembles were enclosed in a grid box exceeding the largest molecule by 5 Å in each direction; a 1 Å step size was preferred to the original coarser 2 Å mesh to reduce the dependency from grid-to-molecule reciprocal orientations. Steric and electrostatic MIFs were computed with Open3DQSAR using MMFF94 van der Waals parameters and charges. The probe constituted a sp3 carbon atom bearing a unit positive charge. Training set MIF data were pre filtered and an energy cut-off was set at 30 kcal mol−1; variables having a standard deviation below 2.0 were discarded; block unscaled weighting was applied to steric and electrostatic fields to give them the same importance in the PLS model. pIC50 values corresponding to the individual molecules were correlated with MIF data for each alignment using PLS regression; the optimal number of principal components (PC) to be extracted was chosen with the same criterion adopted by Tosco et al.,51 namely the one giving rise to the best leave-one-out cross-validation performance, expressed as qLOO2. Finally, the predictive power of each PLS model was evaluated against the external test set and expressed both as Rpred2 and as standard deviation of the error of prediction (SDEP).4.6 Electrochemical studies
The cyclic voltammetry experiments were carried out with a CH Instruments (USA) model 620C potentiostat, and the scan rate was 50 mV s−1. A three-electrode system was used, consisting of a working glassy carbon electrode, 3 mm diameter, an Ag/AgCl reference electrode (3 M KCl), and a platinum wire auxiliary electrode. The glassy carbon electrode was cleaned up by polishing with alumina on a polishing felt (BAS polishing kit). All experiments were conducted at room temperature (25 ± 2 °C) under purging with nitrogen. The compounds (1.0 mM) were dissolved in 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium perchlorate (TBAP) in dimethylformamide (DMF).Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Fondecyt (Grants 1110749 and 1120128), KV thanks to PROMEP-México (Grant 103.5/10/5345), CSIC-UdelaR (Proyecto Grupos No. 661) of Uruguay, MP is grateful to the PEDECIBA-UDelaR Master in Bioinformatics. JV and EB thank ANII (Uruguay) for their scholarships. JSD acknowledges support from Post-Doctoral fellow Fondecyt (Grant 3130359).Notes and references
- P. J. Hotez, PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis., 2007, 1, e149 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. P. Montgomery, M. C. Starr, P. T. Cantey, M. S. Edwards and S. K. Meymandi, Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 2014, 90, 814 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Rodriguez-Guerineau, K. M. Posfay-Barbe, M. Monsonis-Cabedo, T. Juncosa-Morros, A. Diana, C. A. Wyler-Lazarevic, B. M. de Tejada, F. Chappuis, V. Fumado-Perez and Y. Jackson, J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis., 2014, 33, 458 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Pinto, S. Pett and Y. Jackson, Aust. Fam. Physician, 2014, 43, 440 Search PubMed.
- W. R. Steele, E. H. Hewitt, A. M. Kaldun, D. E. Krysztof, R. Y. Dodd and S. L. Stramer, Transfusion, 2014, 54, 2092 CrossRef PubMed.
- www.who.int/neglected_disease/disease/chagas/en.
- L. Murcia, B. Carrilero and M. Segovia, Rev. Esp. Quimioter., 2012, 25, 1 Search PubMed.
- R. Viotti, B. Alarcon de Noya, T. Araujo-Jorge, M. J. Grijalva, F. Guhl, M. C. Lopez, J. M. Ramsey, I. Ribeiro, A. G. Schijman, S. Sosa-Estani, F. Torrico, J. Gascon and N. Latin American, Network for Chagas Disease, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2014, 58, 635 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. V. Pinto and S. L. de Castro, Molecules, 2009, 14, 4570 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. O. Salas, M. Faundez, A. Morello, J. D. Maya and R. A. Tapia, Curr. Med. Chem., 2011, 18, 144 CrossRef CAS.
- M. L. Bolognesi, F. Lizzi, R. Perozzo, R. Brun and A. Cavalli, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2008, 18, 2272 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. A. Tapia, C. O. Salas, K. Vazquez, C. Espinosa-Bustos, J. Soto-Delgado, J. Varela, E. Birriel, H. Cerecetto, M. Gonzalez and M. Paulino, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2014, 24, 3919 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Sieveking, P. Thomas, J. C. Estevez, N. Quinones, M. A. Cuellar, J. Villena, C. Espinosa-Bustos, A. Fierro, R. A. Tapia, J. D. Maya, R. Lopez-Munoz, B. K. Cassels, R. J. Estevez and C. O. Salas, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2014, 22, 4609 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. A. Tapia, L. Alegria, C. D. Pessoa, C. Salas, M. J. Cortes, J. A. Valderrama, M. E. Sarciron, F. Pautet, N. Walchshofer and H. Fillion, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2003, 11, 2175 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Salas, R. A. Tapia, K. Ciudad, V. Armstrong, M. Orellana, U. Kemmerling, J. Ferreira, J. D. Maya and A. Morello, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2008, 16, 668 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Aboul-Fadl, F. A. Bin-Jubair and O. Aboul-Wafa, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2010, 45, 4578 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. J. Chen and N. Foloppe, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2008, 48, 1773 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Prachayasittikul, R. Pingaew, A. Worachartcheewan, C. Nantasenamat, S. Prachayasittikul, S. Ruchirawat and V. Prachayasittikul, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2014, 84, 247 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. R. Duchowicz, D. O. Bennardi, D. E. Bacelo, E. L. Bonifazi, C. Rios-Luci, J. M. Padron, G. Burton and R. I. Misico, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2014, 77, 176 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. P. Jimenez Villalobos, R. Gaitan Ibarra and J. J. Montalvo Acosta, J. Mol. Graphics Modell., 2013, 46, 105 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. A. Hillard, F. C. de Abreu, D. C. Ferreira, G. Jaouen, M. O. Goulart and C. Amatore, Chem. Commun., 2008, 2612 RSC.
- J. M. Miguel del Corral, M. A. Castro, M. Gordaliza, M. L. Martin, A. M. Gamito, C. Cuevas and A. S. Feliciano, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2006, 14, 2816 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Hussain, K. Krohn, I. Ahmed, S. Draeger, B. Schulz, S. Pietro and G. Pescitelli, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2012, 9, 1783 Search PubMed.
- T. A. D. Mendes, J. L. R. Cunha, R. D. Lourdes, G. F. R. Luiz, L. D. Lemos, A. R. R. dos Santos, A. C. J. da Camara, L. M. D. Galvao, C. Bern, R. H. Gilman, R. T. Fujiwara, R. T. Gazzinelli and D. C. Bartholomeu, PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis., 2013, 7, e2524 Search PubMed.
- E. Torres, E. Moreno-Viguri, S. Galiano, G. Devarapally, P. W. Crawford, A. Azqueta, L. Arbillaga, J. Varela, E. Birriel, R. Di Maio, H. Cerecetto, M. Gonzalez, I. Aldana, A. Monge and S. Perez-Silanes, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2013, 66, 324 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Alvarez, J. Varela, P. Marquez, M. Gabay, C. E. Arias Rivas, K. Cuchilla, G. A. Echeverria, O. E. Piro, M. Chorilli, S. M. Leal, P. Escobar, E. Serna, S. Torres, G. Yaluff, N. I. Vera de Bilbao, M. Gonzalez and H. Cerecetto, J. Med. Chem., 2014, 57, 3999 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Nwaka and A. Hudson, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2006, 5, 941 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. J. Romanha, S. L. Castro, N. Soeiro Mde, J. Lannes-Vieira, I. Ribeiro, A. Talvani, B. Bourdin, B. Blum, B. Olivieri, C. Zani, C. Spadafora, E. Chiari, E. Chatelain, G. Chaves, J. E. Calzada, J. M. Bustamante, L. H. Freitas-Junior, L. I. Romero, M. T. Bahia, M. Lotrowska, M. Soares, S. G. Andrade, T. Armstrong, W. Degrave and A. Andrade Zde, Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz, 2010, 105, 233 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Kovacic, Med. Hypotheses, 2007, 69, 510 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. R. Henry and K. B. Wallace, Arch. Toxicol., 1996, 70, 482 CrossRef CAS.
- P. J. O’Brien, Chem.-Biol. Interact., 1991, 80, 1 CrossRef.
- J. Benites, J. A. Valderrama, K. Bettega, R. C. Pedrosa, P. B. Calderon and J. Verrax, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2010, 45, 6052 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Gutteridge and B. Halliwell, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 2000, 899, 136 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. F. Turrens, Mol. Aspects Med., 2004, 25, 211 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Gonzalez-Chavez, V. Olin-Sandoval, J. S. Rodiguez-Zavala, R. Moreno-Sanchez and E. Saavedra, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2015, 1850, 263 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Olin-Sandoval, R. Moreno-Sanchez and E. Saavedra, Curr. Drug Targets, 2010, 11, 1614 CrossRef CAS.
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), 2013, 08, Chemical Computing Group Inc., 1010 Sherbooke St. West, Suite #910, Montreal, QC, Canada, H3A 2R7, 2013.
- E. H. G. da Cruz, C. M. B. Hussene, G. G. Dias, E. B. T. Diogo, I. M. M. de Melo, B. L. Rodrigues, M. G. da Silva, W. O. Valenca, C. A. Camara, R. N. de Oliveira, Y. G. de Paiva, M. O. F. Goulart, B. C. Cavalcanti, C. Pessoa and E. N. da Silva, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2014, 22, 1608 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. B. T. Diogo, G. G. Dias, B. L. Rodrigues, T. T. Guimaraes, W. O. Valenca, C. A. Camara, R. N. de Oliveira, M. G. da Silva, V. F. Ferreira, Y. G. de Paiva, M. O. F. Goulart, R. F. S. Menna-Barreto, S. L. de Castro and E. N. da Silva, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2013, 21, 6337 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. M. Frank, A. B. Ciccarelli, M. Bollini, A. M. Bruno, A. Batlle and M. E. Lombardo, J. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med., 2013, 2013, 10 Search PubMed.
- J. Rodriguez, A. Gerpe, G. Aguirre, U. Kemmerling, O. E. Piro, V. J. Aran, J. D. Maya, C. Olea-Azar, M. Gonzalez and H. Cerecetto, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2009, 44, 1545 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. C. de Abreu, P. A. D. Ferraz and M. O. F. Goulart, J. Braz. Chem. Soc., 2002, 13, 19 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Recabarren-Gajardo, M. Gacitua, I. Murueva, J. Romero, C. Espinosa-Bustos, J. Mella-Raipan, M. A. del Valle, C. D. Pessoa-Mahana and R. Tapia, J. Phys. Org. Chem., 2011, 24, 1179 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. S. Guin, S. Das and P. C. Mandal, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2008, 3, 1016 CAS.
- E. N. da Silva, M. A. B. F. de Moura, A. V. Pinto, M. D. F. R. Pinto, M. C. B. V. de Souza, A. J. Araujo, C. Pessoa, L. V. Costa-Lotufo, R. C. Montenegro, M. O. de Moraes, V. F. Ferreira and M. O. F. Goulart, J. Braz. Chem. Soc., 2009, 20, 635 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Vicente, P. R. Duchowicz, D. Benitez, E. A. Castro, H. Cerecetto, M. Gonzalez and A. Monge, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2010, 20, 4831 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Vera-Divaio, A. C. Freitas, H. C. Castro, S. de Albuquerque, L. M. Cabral, C. R. Rodrigues, M. G. Albuquerque, R. C. Martins, M. G. Henriques and L. R. Dias, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2009, 17, 295 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Aguirre, M. Boiani, E. Cabrera, H. Cerecetto, R. Di Maio, M. Gonzalez, A. Denicola, C. M. Sant’anna and E. J. Barreiro, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2006, 41, 457 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Tosco and T. Balle, J. Mol. Model., 2011, 17, 201 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Tosco, T. Balle and F. Shiri, J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des., 2011, 25, 777 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Tosco and T. Balle, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2012, 52, 302 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c5ra10122k |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |