Biodegradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene with Rhodococcus pyridinivorans NT2: characteristics, kinetic modeling, physiological responses and metabolic pathway†
Debasree Kundu,
Chinmay Hazra and
Ambalal Chaudhari*
School of Life Sciences, North Maharashtra University, P.B. No. 80, Jalgaon 425 001, Maharashtra, India. E-mail: ambchasls@gmail.com; ambchasls@yahoo.com; Tel: +91 257 2257425
First published on 22nd April 2015
Abstract
2,4-Dinitrotoluene (2,4-DNT), a major by-product during the synthesis of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, is widely used as a gelatinizing, waterproofing and plasticizing agent in explosives and propellants. Since DNTs and its metabolites exhibit toxicity to human beings, fish, algae and microorganisms, they are treated as priority pollutant in several countries. This study describes the biodegradation of 2,4-DNT in batch mode by Rhodococcus pyridinivorans NT2 in the range of 0.5–2 mM. At initial concentration of 0.54 mM, degradation kinetics were described well by zero-order model. However, modeling of the biodegradation at higher concentrations indicated that the Andrews–Haldane model predicts the experimental data fairly well. During growth and biodegradation, changes in saturated/unsaturated ratio of fatty acids, total cyclo fatty acids, and the ratio of anteiso:iso-branching were observed. This was accompanied by increased cell size, alternation in enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant defense systems, accumulation of biosurfactants and carotenoids. Biodegradation of 2,4-DNT by this strain proceeded through a pathway involving intermediates such as 2-amino-4-nitrotoluene and 2,4-diaminotoluene. The strain NT2 harbored plasmid that was found to be associated with biodegradation.
1. Introduction
The contamination of soil and water with explosives, especially nitroaromatic compounds such as nitrotoluenes (NTs), is a widespread problem due to accidental spills, industrial effluents, explosive ammunitions and/or from other anthropogenic sources.1–3 2,4- and 2,6-dinitrotoluenes (DNTs), for instance, are by-products of chemical explosives manufacturing (e.g., precursors of TNT in the process of nitration) and are also intermediates in production of herbicides, dyes, and synthetic foams.4 Due to the relatively wide distribution of these manufactures, DNT-associated soil and groundwater pollution remain a critical issue. According to the Toxics Release Inventory, 8159 pounds of 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT were released into the environment from five processing facilities, and there are at least 122 current or former EPA National Priorities List hazardous waste sites that contain 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT.5 2,4-DNT was detected at concentrations of 70–80 mg kg−1 soil in these munitions manufacturing facilities or in the immediate vicinity of firing points.6,7 In China, more than 500 TNT producing plants generated a high number of mono-nitrotoluenes and dinitrotoluenes, which caused pollution of water resources.8 Oral LD50 values for 2,4-DNT range from 268 to 650 mg kg−1 for rats, from 1250 to 1954 mg kg−1 for mice and the reported 14 day LC50 for guppy (Poecilia reticulate) are 12.5 mg l−1.9,10 Due to its abundance, toxicity, mutagenicity and carcinogenicity, 2,4-DNT is treated as a priority pollutant in the US-EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) list11 and are regulated under the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) at low levels. The EPA drinking water standards and the CFR standards required for industrial waste streams are 0.27 and 1.76 μM, respectively.10,12To date, biodegradation of DNTs has been the subject of extensive study because of rapid adaptability of bacterial strains for degradation of such recalcitrant compounds.1–3,11 Since the nitroaromatics are emerging pollutant to the environment, the microbial pathways are still in the early stages of protein/gene evolution.1,2 The first bacterial strain capable of complete 2,4-DNT mineralization was reported only 20 years ago.13 Biotransformation of DNT occurs both by oxidation and reduction. The oxygenase or peroxidise enzymes initiate ring cleavage and the end products of aerobic biooxidation are CO2, NO2−, and cells.14 With reduction, the products include 2-amino-4-nitrotoluene, 4-amino-2-nitrotoluene, 2,4-diaminotoluene, azoxytoluene isomers, and 4-acetamido-2-nitrotoluene.15,16 The reductive reactions are catalyzed by either oxygen-sensitive or insensitive type of non-specific nitroreductases.17 Oxidative and reductive transformations may or may not operate simultaneously.14 Although 2,4-DNT transformation under aerobic conditions can lead to accumulation of reduced transformation products, such finding has only been demonstrated with strains that cannot mineralize 2,4-DNT and when an excess of readily assimilable primary carbon source is present.18 Previous studies on DNT biotransformation under anaerobic conditions indicate that the compound is readily reduced to nitrosonitrotoluenes, aminonitrotoluenes, and 2,4-diaminotoluene.9,14,16 The biotransformability of 2,4-diaminotoluene is largely unknown, although subsequent aerobic oxidation is reported in activated sludge.14 Up till now, aerobic mineralization has been reported with only two organisms, a Pseudomonad strain13 and Phanerochaete chrysosporium.19 Under anaerobic conditions, non-specific reduction does not lead to the ring cleavage reaction and thus mineralization of DNTs has not been demonstrated to date.20 Furthermore, 2,4-DNT degrading microbes are known to yield very small biomass, apparently because several intermediates of its catabolism are known uncouplers of respiration and oxidative phosphorylation.15,21 In addition, most of the studies on biotransformation of DNTs is based on flask biotreatability studies and only a few bacteria are capable of complete biomineralization of DNTs.22,23 While it is well documented that bacteria such as Burkholderia, Pseudomonas, Desulfovibrio24 or fungus P. chrysosporium19 are able to degrade 2,4-DNT, to the best of our knowledge, this has not been previously reported for Rhodococcus.
In an ongoing effort towards the objective to enlarge the scope of microbes in bioremediation, we have isolated, screened and identified a R. pyridinivorans strain NT2 for the degradation of 4-NT and DNTs.25,26 However, further details of biochemical, physiological and molecular changes involved in the resistance of this strain NT2 towards elevated concentrations of DNTs have remained uncharacterized so far. The earlier studies mostly pivoted around degradation of NTs by non-actinomycetes and Gram negative bacteria, particularly Pseudomonas from contaminated soil, groundwater and wastewater treatment plants.2 However, Gram positive actinobacteria are rarely reported since (i) thick cell wall architecture may hinder mass transfer and can result in low degradation inside the cell, (ii) longer growth cycle likely to prolong the overall degradation time, and (iii) no efforts on biokinetics, biodegradation pathways and bioavailability considerations were taken to unravel low rate of NTs biodegradation. Therefore the aims of this work were (i) to assess the growth dynamics and aerobic biodegradation of 2,4-DNT by the previously isolated 4-NT degrading R. pyridinivorans strain NT2, (ii) to investigate the metabolic perturbations involved during tolerance of 2,4-DNT by examining alterations in cell morphology, fatty acid composition of membrane, antioxidant defense mechanism, involvement of extracellular tensioactive metabolites and accumulation of carotenoids and (iii) elucidation of major metabolites involved in the catabolic pathway(s).
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Chemicals
2,4-DNT [CH3C6H3(NO2)2, CAS#121-14-2, 97%] was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH (Steinheim, Germany). 2-amino-4-NT, 2-amino-6-NT, 2,4-diaminotoluene, and 2,6-diaminotoluene were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Methanol and chloroform were purchased from Merck, Mumbai, India. All other chemicals were procured from HiMedia, Mumbai (India). All other chemical reagents used were of analytical grade.2.2. Microorganism and culture conditions
Rhodococcus pyridinivorans NT2, isolated from pesticides contaminated effluent-sediment, was used in this study. For all experiments, cells were grown in mineral salt basal (MSB) medium (pH 7.0 ± 0.2)25 supplemented with filter-sterilized 2,4-DNT (100 mg l−1, i.e. 0.54 mM from stock solution in acetone), wherever not mentioned. Acetone was removed by evaporation prior to the addition of the aqueous medium. The biomass was harvested by centrifugation (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 rpm for 10 min) and washed twice with sterile saline. The washed cells were then suspended in assay medium to a final density of O.D600 = 0.5 (corresponding to 1.6 mg cdw l−1; cdw: cell dry weight).
000 rpm for 10 min) and washed twice with sterile saline. The washed cells were then suspended in assay medium to a final density of O.D600 = 0.5 (corresponding to 1.6 mg cdw l−1; cdw: cell dry weight).
The isolate was maintained by routine bimonthly transfer under aseptic conditions to an inorganic MSB medium provided with 2,4-DNT (0.54 mM) as sole source of carbon, nitrogen and energy and stored at 4 °C after incubation at 30 °C for 48 h.
2.3. Culture growth on 2,4-DNT and substrate utilization kinetics
Growth kinetics of strain NT2 was determined in batch flasks at a 2,4-DNT concentration of 0.5–2 mM using 2,4-DNT as a sole substrate. A stock solution of 2,4-DNT was prepared by dissolving the required mass of 2,4-DNT crystals in acetone. This solution was filter sterilized through 0.2 μm nylon filter. An appropriate aliquot of this stock solution was transferred into sterile 500 ml conical flasks using a micro syringe. These flasks were left for a few hours in the fume hood sealed with cotton wool so as to allow the solvent to evaporate. MSB medium (100 ml; pH 7.0 ± 0.2) was added after complete evaporation of the solvent. 2,4-DNT grown NT2 strain taken from mid log phase was harvested by centrifugation, washed and resuspended in phosphate buffer to obtain an OD of 0.5. Aliquots of this cell suspension (2.5 ml) were added to flasks containing 2,4-DNT in MSB media. After inoculation the flasks were incubated in a rotary shaker (120 rpm) set at 30 °C. Uninoculated control flasks were also kept to account for abiotic loss of 2,4-DNT. Growth study at a fixed 2,4-DNT concentration was conducted in multiple batch flasks. Excess NTs suspended in the aqueous phase was found to have negligible effect on absorbance measurement as revealed through measurements in control flasks that were not inoculated with the bacterial culture. The residual substrate in the culture medium was calculated using the formula:
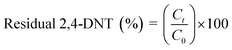 | (1) |
2.4. Physiological and cellular responses of R. pyridinivorans NT2 growing on 2,4-DNT
The polynomial responses of the strain following exposure to 2 mM of 2,4-DNT was assessed in terms of (i) alteration in total cellular fatty acid composition, (ii) morphometric analysis of cell morphology, (iii) extracellular secretion of tensioactive biosurfactants, (iv) detection of electron transport system (ETS) activities, analysis of catalase (E.C. 1.11.1.6), glutathione-s-transferase (GST) (E.C. 2.5.1.18), superoxide dismutase (E.C. 1.15.1.1) and DPPH radical scavenging activities, and (v) total content of carotenoid accumulated in the cells. These are detailed in ESI.†2.5. Analytical methods
Cell growth was monitored by measuring the optical density at 600 nm using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (model no. 1601, Shimadzu, Japan). OD600 values were then converted into dry cell mass (mg l−1) using an appropriate calibration curve.Samples were withdrawn at fixed time intervals during degradation studies, appropriately diluted; biomass removed by centrifugation at 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 rpm and initial monitoring was done by TLC on silica gel G plates using toluene
000 rpm and initial monitoring was done by TLC on silica gel G plates using toluene![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate
ethyl acetate![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) acetic acid (60
acetic acid (60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30
30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10, v/v/v) as mobile phase and were visualized under ultraviolet (UV) light (A254). High performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) analyses of each sample were performed on a CAMAG system (CAMAG, Switzerland) as per Kulkarni and Chaudhari.28
10, v/v/v) as mobile phase and were visualized under ultraviolet (UV) light (A254). High performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) analyses of each sample were performed on a CAMAG system (CAMAG, Switzerland) as per Kulkarni and Chaudhari.28
At any time, residual 2,4-DNT was analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).10 A sample mixture was prepared by taking 0.7 ml of a sample and mixing it with 0.7 ml of acetonitrile. The resulting mixture was vortexed, and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 min, and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.2 μm membrane filter. The filtrate was analyzed for 2,4-DNT using a HPLC (Shimadzu, Japan) equipped with SPD-10AVP UV-detector set at 254 nm. The mobile phase was methanol![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) water mixture (50
water mixture (50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50, v/v), and 20 μl samples were injected into a silica gel-packed C18 column [dimension: 4.6 mm (i.d) 0 250 mm (l)] of particle size (5 μm) (Phenomenex) at 25 °C. The flow rate of the solvent was set to 1.0 ml min−1. The 2,4-DNT concentration in samples was then estimated based on calibration curves obtained using a standard.
50, v/v), and 20 μl samples were injected into a silica gel-packed C18 column [dimension: 4.6 mm (i.d) 0 250 mm (l)] of particle size (5 μm) (Phenomenex) at 25 °C. The flow rate of the solvent was set to 1.0 ml min−1. The 2,4-DNT concentration in samples was then estimated based on calibration curves obtained using a standard.
The concentrated extracts from samples withdrawn at periodic intervals were also submitted for GC-MS analysis using a Shimadzu QP2010 Plus apparatus equipped with quadruple mass filter Rtx-5MS capillary column (30 m × 0.25 mm), scan interval 0.5 s and mass range 40–500 m/z. The temperature programme was held at 50 °C for 1 min with 20 °C increase min−1 to a final temperature 280 °C for 14.5 min and the injector temperature was kept at 250 °C. The injection volume was 1 μl and the carrier gas was helium. The metabolites were identified by comparing GC retention time with standard compounds and fragmentation pattern of either authentic compounds or those present in the NIST library.
Nitrate was analyzed using spectrophotometric method at 275 nm following Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater.29 Nitrite was assayed by Griess reaction as described by Montgomery and Dymock.30
2.6. Plasmid isolation and detection
A loopful of culture was grown in nutrient broth at 30 °C for 18 h and centrifuged (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 rpm, 10 min). Plasmid was isolated from the cell mass by small scale alkaline lysis method.31 To monitor spontaneous loss of plasmid(s) cells were grown in nutrient broth for approximately 50 cell divisions with frequent media replacement. Cultures were then diluted and spread on nutrient agar plates. Curing of plasmid was performed by growing the culture in the presence of ethidium bromide (500 μg ml−1) for 24 h at 30 °C or 40 °C and then plated on nutrient agar plates to obtain isolated colonies. The isolated colonies were then replica plated on nutrient agar and MSB agar containing 2,4-DNT (0.54 mM). The colonies that failed to grow on MSB agar plates were considered as putative cured derivatives. The physical loss of plasmid in the cured derivatives was confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis. The percentage curing efficiency was expressed as number of colonies with cured phenotype per 100 colonies tested. E. coli DH5α was transformed with purified plasmid DNA from R. pyridinivorans NT2 by the heat shock method as described previously.32 Competent E. coli DH5α cells were prepared as per Current Protocols in Molecular Biology.32 Transformants were selected on MSB agar containing 2,4-DNT (0.54 mM) as sole source of carbon and energy. E. coli DH5α competent cells were spread on the same medium as negative control.
000 rpm, 10 min). Plasmid was isolated from the cell mass by small scale alkaline lysis method.31 To monitor spontaneous loss of plasmid(s) cells were grown in nutrient broth for approximately 50 cell divisions with frequent media replacement. Cultures were then diluted and spread on nutrient agar plates. Curing of plasmid was performed by growing the culture in the presence of ethidium bromide (500 μg ml−1) for 24 h at 30 °C or 40 °C and then plated on nutrient agar plates to obtain isolated colonies. The isolated colonies were then replica plated on nutrient agar and MSB agar containing 2,4-DNT (0.54 mM). The colonies that failed to grow on MSB agar plates were considered as putative cured derivatives. The physical loss of plasmid in the cured derivatives was confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis. The percentage curing efficiency was expressed as number of colonies with cured phenotype per 100 colonies tested. E. coli DH5α was transformed with purified plasmid DNA from R. pyridinivorans NT2 by the heat shock method as described previously.32 Competent E. coli DH5α cells were prepared as per Current Protocols in Molecular Biology.32 Transformants were selected on MSB agar containing 2,4-DNT (0.54 mM) as sole source of carbon and energy. E. coli DH5α competent cells were spread on the same medium as negative control.
2.7. Statistical analyses
Data are reported as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. For biodegradation assays, statistical analysis of differences was carried out by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). All analyses were performed using Minitab statistical software (release 16; Minitab Inc., State College, PA). P < 0.05 was considered to indicate significance.3. Results and discussion
3.1. Effect of acclimatization of R. pyridinivorans NT2
NTs serve as a substrate and a toxicant simultaneously.33 Cells grow readily on the mono-NTs within a level of concentration but are inhibited by even low concentration of 2,4- and 2,6-DNT. The cell required different time with initial concentration of 2,4-DNT (Table S1 in ESI†). Before acclimatization, the bacterial cells were able to grow and degrade 1 mM 2,4-DNT within 72 h, while at higher 2,4-DNT concentrations cell lysis occurred. However, the acclimatized culture could degrade 1.2 and 1.4 mM 2,4-DNT within 72 h, 1.6 and 1.8 mM 2,4-DNT within 96 h, and eventually completely degraded 2 mM 2,4-DNT within 120 h with no signs of cell lysis (Fig. S1; ESI†).Once the effect of gradual increment of 2,4-DNT concentration was established, effect of repeated exposures to a same concentration was also examined. It was observed that two or three times of exposure to the same concentration of 2,4-DNT resulted in negligible increase in the degradation rate. This finding is in accordance with previous reports on phenol degradation.34 Two key aspects mainly govern microbial acclimatization during biodegradation: (i) change of cell membrane composition35,36 and (ii) induction of intracellular enzyme titre which controls overall catabolic reaction rate.34,37,38 Since the isolate NT2 followed a reductive metabolic pathway (see later in Fig. 6), nitroreductase enzyme activities were measured at different initial 2,4-DNT concentrations. As shown in Table S2 (ESI†), 1 mM 2,4-DNT induced higher enzyme activity than 0.5 mM 2,4-DNT by 18–27% throughout degradation stages; but, nitroreductase titre was lower in 2 mM 2,4-DNT grown cells as compared to cells grown on 1 mM 2,4-DNT. These observations may explain why cells pre-exposed to 0.5 mM 2,4-DNT degraded 1 mM 2,4-DNT in 48 h while 2 mM 2,4-DNT was degraded in 120 h. Nonetheless, it needs more investigation to validate these phenomena.
3.2. Growth kinetics and biodegradation profile of 2,4-DNT at low and high concentration by strain NT2
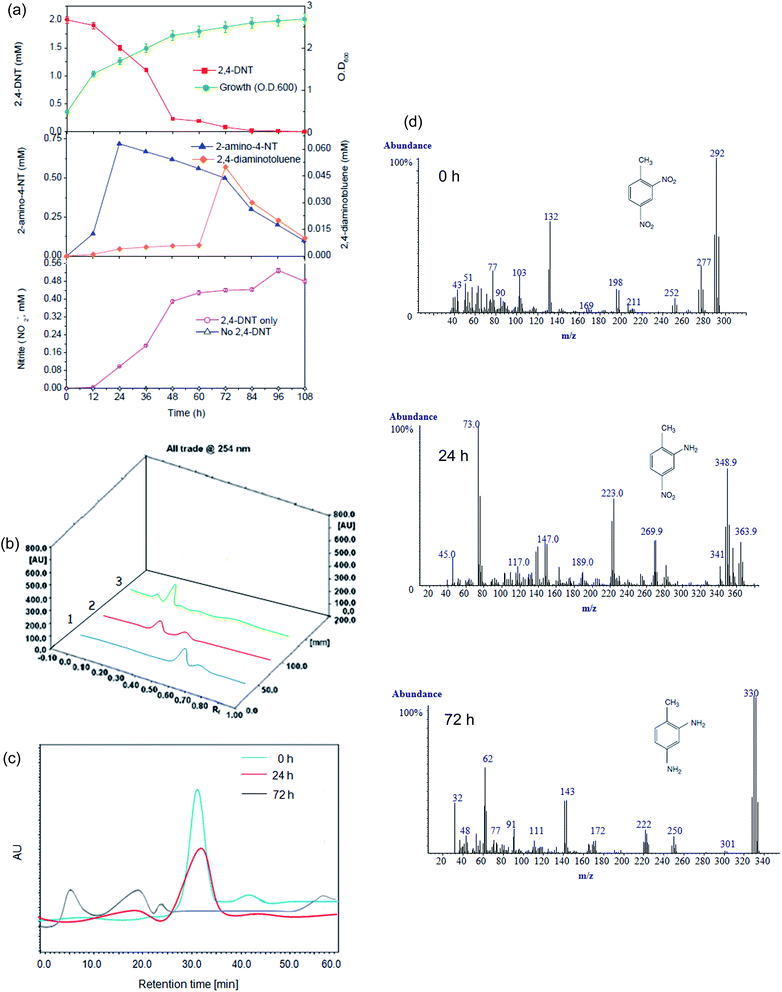
At an initial concentration of 100 mg l−1 (i.e. 0.54 mM), acclimated cells of strain NT2 at 0.5 OD (A600) was capable of degrading 2,4-DNT within 48 h with a calculated growth yield and degradation rate of 0.68 (±0.04) g of cells g−1 and 1.38 mg l−1 h−1, respectively. The growth of strain NT2 fitted well according to the logistic model (R2 = 0.99; Fig. S2; ESI†). The degradation of 2,4-DNT (100 mg l−1) was fitted with the four mathematical kinetic models as shown in Fig. S3 (ESI†). The degradation kinetics of 2,4-DNT by NT2 can be described well by zero-order reaction (R2 = 0.977) kinetics. The calculated degradation rate constant (K) was 7.87 h−1 and the theoretical half-life (t1/2) was 0.08 h.This scenario continued even at higher concentration of 2,4-DNT (1–2 mM). Time course progress curves using NT2 cells at 0.5 OD (A600) in MSB media showed (i) almost no lag phase during growth, (ii) complete degradation effected in 108 h with an degradation rate of 0.018 mM h−1, and (iii) and the biomass appreciably increased from 0.5 OD (1.6 mg cdw l−1) to 2.68 OD units (8.57 mg cdw l−1) (Fig. 1). In all the studies, abiotic loss of 2,4-DNT determined in the uninoculated control flasks was in the range of 0–10%.
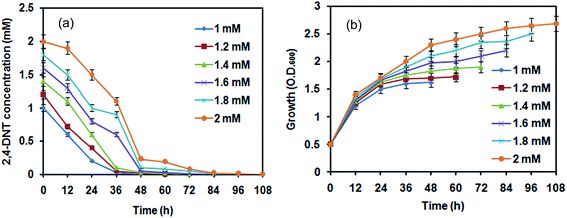 | ||
| Fig. 1 (a) Degradation of 2,4-DNT and (b) growth profile of R. pyridinivorans NT2. Data are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Small (non-visible) standard deviations are within the symbols. | ||
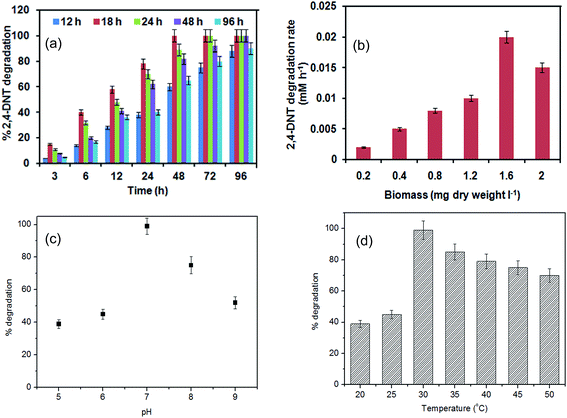
3.3. Effect of operational parameters on growth of 2,4-DNT degrading strain NT2
3.4. Kinetic modeling and parameter identifiability for the growth kinetics of R. pyridinivorans NT2 in the presence of 2,4-DNT
Fig. 3 shows the specific growth rate (μ) and the rate of substrate consumption (RS) for different initial concentration of 2,4-DNT. A typical trend was observed in which specific growth rates first increased with the increase in initial concentrations of 2,4-DNT up to a certain concentration level, and then decreased with increase in the concentrations. When grown on 2,4-DNT, the maximum experimental specific growth rate was found to be 0.1 h−1 at 2 mM. The decline trend of specific growth rates beyond this initial concentration confirmed that substrate inhibition occurred. Although no comparison with previous literature could not been made due to paucity of data, these results agree with those reported for other inhibitory substrates by different bacteria,35–38 yeast,40,41 and filamentous fungi.42,43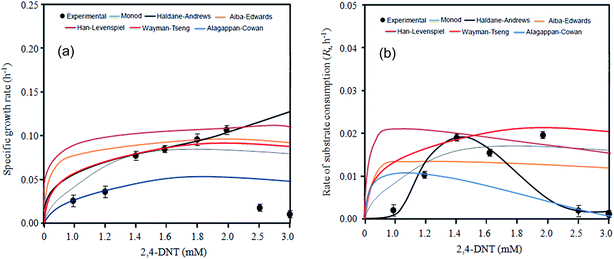 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a) Experimental specific initial growth rate and (b) substrate degradation rate profile during biodegradation of 2,4-DNT by strain NT2. | ||
Relatively very few data exist in the literature about the rate of substrate consumption (RS) and most of the information available deals with the specific growth rate. Therefore, substrate degradation rates (RS) were calculated and plotted against initial 2,4-DNT amount.
Here, the initial substrate degradation rates increases with initial substrate concentrations reaching a maximum and then decreases due to inhibition. The maximum degradation rate and the maximum growth rate were observed at 2 mM. These results are relevant since the objective of this work is to treat the toxic wastewater, rather than growing the bacteria. Values of kinetic constants for biodegradation of 2,4-DNT using six growth kinetic models are listed in Table 1. On the basis of the goodness-of-fit tests, the Andrews–Haldane inhibitory model obviously yielded a much better fit to a reasonable level of accuracy (correlation coefficient, R2 = 0.87 and 0.83 for μ and Rs, respectively) than the other models.
| Model | Parameters obtained for specific growth rate (μ) | Parameters obtained for specific degradation rate (Rs) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μmax (h−1) | Ks (mg l−1) | Ki (mg l−1) | μ*max (h−1) | Sm (mg l−1) | m | n | R2 | Rs max (h−1) | K′s (mg l−1) | K′i (mg l−1) | R*s max (h−1) | R2 | |
| a ND: not determined. | |||||||||||||
| Monod | 0.008 | 15.33 | ND | 0.007 | ND | ND | ND | 0.43 | 0.011 | 2.21 | ND | 0.009 | 0.48 |
| Andrews–Haldane | 0.011 | 28.46 | 574 | 0.01 | 378 | ND | ND | 0.87 | 0.018 | 2.33 | 1.79 | 0.016 | 0.83 |
| Aiba–Edwards | 0.021 | 22.39 | 373 | 0.009 | ND | ND | ND | 0.31 | 0.012 | 1.06 | 2.41 | 0.010 | 0.51 |
| Han–Levenspiel | 0.028 | 24.55 | ND | 0.022 | 369 | 1 | 0.18 | 0.44 | 0.02 | 1.35 | 2.88 | 0.007 | 0.72 |
| Wayman–Tseng | 0.007 | 31.47 | ND | 0.005 | ND | ND | ND | 0.35 | 0.015 | 2.11 | 2.11 | 0.009 | 0.71 |
| Alagappan–Cowan | 0.006 | 41.68 | 657 | 0.005 | ND | ND | ND | 0.78 | 0.017 | 1.08 | 1.67 | 0.014 | 0.66 |
Using Andrews–Haldane model, the fitting parameter μmax (0.011 h−1), μ*max (0.01 h−1) and Sm (378 mg l−1) were calculated. When we calculated Sm from data given in the literature and compared these values to those obtained for strain NT2, we observed that Sm from this study was among the highest values obtained for pure cultures, which is an advantage for further treatment of nitroaromatics contaminated water. However, the μmax was low when compared with other microorganisms. Nevertheless, this shortcoming is counterbalanced by the strain's ability to tolerate and degrade NTs at high concentration as well as its ability to degrade different types of toxicants.25,26 In most of the works reported in the literature, a discrepancy is observed between the graphical determination and the calculated value of μmax.41,44 The difference between μmax and μ*max was already reported, for example by Christen et al.44 and Shareefdeen et al.45 during phenol and methanol biodegradation, respectively. Generally, in the literature, the values reported for μmax are overestimated with respect to the true μmax (μ*max), in a range varying from 24% to more than 100%.44 It is certain that the data from both this study and previous ones show a clear inhibitory phase beyond a threshold substrate concentration, although the substrate concentration range for appearance of inhibitory phase differed from one to another study in the literature. The inhibition constant (Ki) obtained in this study is in the middle range of values reported in the literature for a pure culture.44 KS describes the ability of a microorganism to grow at low concentration. Most of the KS values found in the literature lie between 1 and 110 mg l−1 and the value reported here was well within this range (Table 1). A high resistance of R. pyridinivorans NT2 as judged from the estimated Ki value may be due to the fact that some actinomycetes form hyphae and large micro colonies as a measure of protecting the inner cell mass which may facilitate easy degradation and tolerance to toxic substrates.46 The combination of KS and Ki shows that, in comparison to other pure cultures generally grown on aromatic compounds, strain NT2 is able to grow on NTs-containing wastewaters within a wide range of concentrations.
The profile of cell mass yield as a function of 2,4-DNT concentration (Fig. S4a; ESI†) was similar to that of specific growth rate. The yield maximized at 2 mM where μ was also maximum. Beyond this point, mass yield coefficient values decreased considerably with increase in concentration of 2,4-DNT. Such decrease in Y with increasing substrate concentration in inhibitory region is in accordance with previous studies.46–48 Also, Y/YE initially remained almost steady up to 2 mM (Fig. S4b; ESI†). Thereafter, the value increased with a raise in concentration of 2,4-DNT. Also, the relative proportion of the substrate consumed for energy (Y/YE) was drastically exceeded than for assimilation into cell mass (Y/YC) for concentrations beyond 2 mM, which could be attributed to the requirement of high-maintenance energy for overcoming the effect of substrate inhibition at high levels.
3.5. Physiological and cellular response of R. pyridinivorans NT2 growing on 2,4-DNT
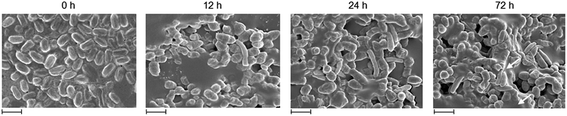
At the cellular membrane level, the main mechanisms of Rhodococcus strains are increase in the degree of saturation of membrane fatty acids and decrease the relative proportion of saturated methyl, cyclopropyl branched fatty acids, and unsaturated fatty acids.49 During growth on 2,4-DNT, the relative % concentration of total saturated fatty acid and cyclic fatty acid increased significantly whereas the amount of total unsaturated fatty acids decreased (Table S3 in ESI†). In a previous study, we found that R. pyridinivorans NT2 cells tolerated 4-NT by increasing the saturated/unsaturated ratio of fatty acids and saturated anteiso/iso ratio, and thus, decreased membrane fluidity.25 Here, cells commonly responded to 2,4-DNT by increasing the saturated/unsaturated ratio of fatty acids, total cyclo fatty acids, and the ratio of anteiso:iso-branching. These observations clearly indicate the putative role of saturated, unsaturated and branched fatty acids in determining the bacterial response towards environmental stress.This marked difference in membrane fatty acids profile is also reflected by the results on morphological level as a mechanism toward stress-induced toxicity. Fig. 4 shows FESEM photographs of R. pyridinivorans cells growing in 2 mM of 2,4-DNT as the sole carbon and energy source. As the cultivation time progressed, the cells increased in size (∼2.5 times) with filamentous appearance having an average size of 2.05–2.17 μm after 72 h as compared to 0.783 μm (0 h) (see Table S4 in ESI†). With increasing cell size, the relative area of their cell envelope decreased so as to reduce the toxic effects and this might be the putative mechanism for tolerance. Also, the smooth surface of the cells (at 0 h) turned into a rough and irregular surface after the degradation process as is prominent in the photographs. Meanwhile, some blebs could be observed at 72 h on the surface of cells grown in the presence of 2,4-DNT. There was progressive accumulation of a matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) at the surfaces of colonies. It could be speculated that the EPS produced in this study might be a biosurfactant. Similar changes in cell morphology coupled with EPS or biosurfactant secretion were reported for isoniazid degrading Mycobacterium smegmatis,50 water stressed R. opacus PD630,51 fluoranthene degrading Rhodococcus sp. BAP-1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 52 and 4-NT degrading R. pyridinivorans.25
52 and 4-NT degrading R. pyridinivorans.25
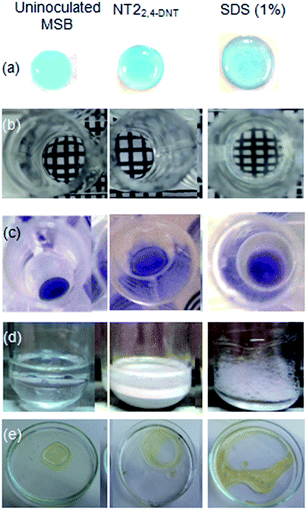
The production of biosurfactant by the strain NT2 was primarily screened by parafilm M, microplate, drop collapse and oil spreading assays (Fig. 5a–c and e). These qualitative tests are indicative of surface activity and wetting properties.53,54 In parafilm M test, the diameter of the cell-free culture supernatant was greater than that of a fresh culture medium and was lesser than SDS (Fig. 5a). In addition, the optical distortion of the grid behind a multiwell plate provided a qualitative assessment in microplate assay (Fig. 5b). In drop collapse assay, the sample droplet will either form bead, spread out slightly or collapse, depending on the amount of surfactant in the sample. Thus, the visual determination of the results of Fig. 5c showed that spreading of the cell-free culture supernatant was nearly same as those of SDS. Further, emulsification index was calculated with toluene (Fig. 5d) to quantify the biosurfactant production. In oil spreading assay, diameter of clearing zone of cell-free culture supernatant on the oil surface (caused due to displacement of oil by surfactant, if present) was much bigger as compared to fresh uninoculated MSB media and indicated that strain NT2 produces biosurfactants that highly reduce the surface tension of the culture medium.
The biosurfactant production started after 12 h and highest emulsification index of 56 ± 0.81% at 48 h was obtained after cultivation on 2,4-DNT. These emulsions were found to be stable for more than a month at room temperature without any change in emulsification index. The surface tension of the culture decreased from 63.2 (±0.5) to 35.5 (±0.3) dyne cm−1. Contact angle of 2,4-DNT grown NT2 was 79.85 (±1.6) at mid-log phase, which indicated moderately hydrophobic cell surfaces. It is yet to be seen whether the biosurfactant detected here is trehalolipids or its isoforms as reported earlier during biodegradation of 4-NT by this strain.25
Data from enzyme activity assays showed the λmax of metabolites for 2,4-DNT-induced cells were 225, 247, 292, 358 nm (corresponded to 2-amino-4-NT) and 210, 294 nm (corresponded to authentic 2,4-diaminotoluene)55 together with the consumption of NADPH (λmax = 340 nm).56 The ETS activity increased by 11.9-fold (125 μmol g min−1) after 48 h from an initial value of 10.5 μmol g min−1 at 0 h. Activities of antioxidant enzymes, i.e. catalase, SOD, GST, and DPPH radical scavenging activity significantly increased as time progressed with respect to control (0 h) (Table S5; ESI†). High levels of ROS produced (as measured from DPPH radical scavenging assay) during growth and degradation of DNT may have resulted in increased activities of these enzymes.
The total carotenoid content was 81 (±1.2) μg g−1 of wet cell weight when grown on 2 mM of 2,4-DNT. The UV-Vis spectra of the orange-coloured pigment in 2,4-DNT grown cells of strain NT2 (Fig. S5; ESI†) after 72 h revealed four major peaks (peak 1, λmax = 455 nm; peak 2, λmax = 460 nm; peak 3, λmax = 470 nm; and peak 4, λmax = 450 nm). The profile of peak 1, 2, 3 and 4 are identical to that of the monocyclic carotenoid 4-keto-γ-carotene, monocyclic carotenoid γ-carotene, lycopene (or diapolycopene) and β-carotene (or diapotorulene), respectively.57 Nevertheless, further detailed structural analysis is necessary to determine specific carotenoids present in the samples. Lipophilic carotenoids either exist intracellularly (e.g., in lipid droplets or in the vicinity of the plasma membrane) or around hydrophobic Rhodococcus cells (due to the presence of aliphatic chains of mycolic acids in the cell wall). With UV-Vis analysis alone, however, the exact location of the orange carotenoids could not be sourced. In microorganisms, carotenoids accumulate as a stress response to intense UV irradiation, high temperature, and the presence of ROS. As R. pyridinivorans NT2 is a nonphotosynthetic bacterium, photosynthetic functions of accumulated carotenoids can be ruled out. Also, it is unlikely that carotenoids serve as a UV light quencher during this study where the culture was not exposed to strong UV light. It seems reasonable that the antioxidant ability of carotenoids is a more plausible scenario for the present finding. As the planktonic cells of strain NT2 develops into biofilm, more oxidative stress would be exerted in individual cells due to an increase in the level of ROS. To counter the increasing oxidative stress, cells would produce and accumulate more carotenoids. This scenario, though only speculative at present, is consistent with works done by earlier workers, which showed that endogenous oxidative stress is central to produce diversity in Pseudomonas and some Rhodococcus biofilms.58
3.6. Identification of putative metabolites during degradation of 2,4-DNT
During growth of NT2 on MSB, complete transformation of the initial 2 mM 2,4-DNT was achieved in 108 h (Fig. 6a). 2,4-DNT disappearance was followed by the production of 2-amino-4-NT and its concentration reached transient maximum in 24 h. This compound was further reduced to the eventual product, 2,4-diaminotoluene, which appeared in 72 h (Fig. 6a). To explore the pathways of 2,4-DNT degradation by this isolate, TLC, HPTLC, HPLC and GC-MS analyses were performed. HPTLC densitogram revealed the presence of 2-amino-4-NT and 2,4-diaminotoluene at 24 h and 72 h (Fig. 6b), respectively. Similarly, examination of HPLC profile of 2,4-DNT grown culture revealed the presence of 2,4-DNT (0 h; Rt = 31.0 min), 2-amino-4-NT (24 h; Rt = 19.0 min) and 2,4-diaminotoluene (72 h; Rt = 6.0 min) (Fig. 6c) which is in good agreement with data of authentic standards and published literature.10,15 The identification of metabolites was further confirmed by comparison of m/z of the molecular ion and fragmentation patterns of the molecular ion from mass spectra (Fig. 6d). The GC-MS analysis of the extracted culture broth of 2,4-DNT containing MSB media revealed the presence of two metabolites, 2-amino-4-NT and 2,4-diaminotoluene, identified by comparing the fragmentation pattern of standard compound present in the NIST library. Evidently, these metabolites were formed due to the conversion of the nitro group to the amino group as a result of a reductive metabolic pathway. Similar reaction pattern has been observed in 2,4-DNT transformation by microorganisms59–62 and plants.16 Although 2,4-DNT transformation under aerobic conditions can lead to accumulation of reduced transformation products, such finding has only been demonstrated with strains that cannot mineralize 2,4-DNT and when an excess of readily assimilable primary carbon source is present. Efforts in unravelling the exact mechanism of biotransformation of 2,4-DNT is currently underway in our laboratory.The observed nitrite (NO2−) concentrations were nearly 15-fold lower than the expected stoichiometric concentrations and neither nitrate (NO3−) nor NH4+ ions were detected (Fig. S6a; ESI†). No NO2− was produced in the absence of 2,4-DNT. The plausible explanation for a lower than expected nitrite accumulation is its conversion into a gaseous form of nitrogen, either N2 or one of the nitrogen oxides, which was observed in previous studies. However, we did not observe any nitrate or NH4+ ions here. In previous studies, N2 was shown to be the main product of aerobic denitrification at pH > 7 whereas NO became the predominant product at pH < 6.15,63 Here the initial pH was set at 7.0 and only a negligible deviation in pH from its initial value was recorded (ΔpH < 0.1). The most likely explanations for lower than expected theoretical nitrite release in the media are (i) incorporation of nitrite-originated nitrogen into biomolecules when NTs was used as the sole C–, N– and energy sources; and (ii) probable utilization of nitrite for biomass growth.15 Nitrite accumulation within the cells is unlikely due to the high toxicity of nitrite. In order to investigate the use of nitrite by the isolate, several 2,4-DNT biodegradation experiments were conducted with and without an artificially added elevated nitrite concentration.
Nitrite removal activity was observed (0.02 mM h−1) both in the presence and absence of 2,4-DNT (Fig. S6b; ESI†). Denitrification in this strain is also corroborated with previous reports wherein R. pyridinivorans is often characterized by expressing nitroreductase.64,65 This is relevant since nitrite released is also an environmental toxic agent.66
The presence of additional nitrite led to only a slight increase of the initial 2,4-DNT degradation rate (Fig. S6b; ESI†). Conversely, the average 2,4-DNT removal rate, by nitrite was slightly reduced in the presence of large nitrite concentrations suggesting nitrogen was not a limiting nutrient. This slight enhancement of the initial 2,4-DNT degradation rate by nitrite indicated that nitrite is partially used by the cells as an oxidant, i.e., an acceptor of electrons, even under aerobic conditions. This is in accordance with Hudcova et al.15
It is significant to study how DNT degradation is affected by the presence of both isomers, since 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT are produced in a 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 ratio, and are therefore often present together in munitions plant wastewater. The observed negative effect of 2,6-DNT on 2,4-DNT degradation (Fig. S6c; ESI†) cannot be explained by catabolic competition because 2,6-DNT is less biodegradable. Perhaps, this effect is due to a higher toxicity of 2,6-DNT to bacterial cells, which could be ameliorated by the presence of 2,4-DNT, a growth substrate.15
1 ratio, and are therefore often present together in munitions plant wastewater. The observed negative effect of 2,6-DNT on 2,4-DNT degradation (Fig. S6c; ESI†) cannot be explained by catabolic competition because 2,6-DNT is less biodegradable. Perhaps, this effect is due to a higher toxicity of 2,6-DNT to bacterial cells, which could be ameliorated by the presence of 2,4-DNT, a growth substrate.15
In previous studies, several mixed or pure microbial cultures were able to degrade 2,4-DNT in either an aerobic oxidative pathway or a reductive pathway that may occur aerobically or anaerobically.14,24,60 Aerobic biodegradation of 2,4-DNT was determined in laboratory slurry reactors, soil columns, and fluidized bed biofilm reactors.67 Under anaerobic processes, 2,4-DNT was removed via fluidized-bed granular activated carbon bioreactors, activated sludge reactors, and immobilized micro-organisms biological filter.61 Comparison of 2,4-DNT transformation by R. pyridinivorans with the reactions in earlier cited works showed comparable reducing activity (Table S6; ESI†). From an environmental impact perspective, members of Rhodococcus genus are widely known for thriving redox-stratified environments where nitroaromatic compounds are readily and strongly sorbed. Based on this, our finding is expected to not only deepen our understanding on the environmental fate, but it is conceivable that the range of nitroaromatic compounds that serves as growth substrates for strain NT2 could be further extended.
3.7. Plasmid characterization
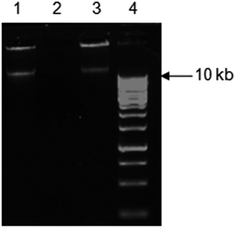
An understanding of the genetic basis of bioremediation activity could provide a basis for predicting the environmental fate of compounds like 2,4-DNT. The involvement of a catabolic plasmid(s) in the degradation of organic compounds has been shown previously for 2,4-D, substituted phenylurea, carbaryl, para-nitrophenol, chloronitrobenzene, atrazine, sulcotrione and 2,4-DNT.11,28,68 Hence, to check if plasmid is present in strain NT2 that could be involved in 2,4-DNT degradation, attempts were made to isolate the plasmid from this strain. Plasmid (Fig. 7; lane 1) was found to be present in NT2. Plasmid DNA can exist in three conformations: supercoiled or covalently closed circular (ccc) DNA, open-circular (oc), and linear. Most preparations of uncut plasmid contain at least two topologically-different forms of DNA, corresponding to supercoiled and nicked circles/open-circular/relaxed forms. A small, compact supercoiled knot of ccc-DNA experiences less friction against the agarose matrix than does a large, floppy open circle of oc-DNA. Thus, for the same over-all size, supercoiled DNA runs faster than open-circular DNA. Linear DNA runs through a gel end first and thus sustains less friction than open-circular DNA, but more than supercoiled. Therefore, an uncut plasmid may produce two bands on a gel, representing the oc and ccc conformations. If the plasmid is cut once with a restriction enzyme, however, the supercoiled and open-circular conformations are all reduced to a linear conformation. In Fig. 7, the two bands in lane 1 and 3 may represent two circular forms of the same plasmid DNA (oc on top, and ccc below). In other words, the slowest moving band in lane 1 and 3 may correspond to the open circular form, whereas the other band might correspond to covalently closed circular forms. In addition, the presence of linear DNA in a plasmid preparation may be a sign of either nuclease contamination or cutting with a restriction enzyme. Presence of nuclease may be ruled out in this case due to the following observations: (i) usual touching the insides of eppendorf lids was avoided; (ii) nuclease free water was used; and (iii) purity of the DNA was checked by A260/A280 ratio. Additionally, restriction enzymes were not used and thus presence of linear DNA may be ruled out. However, the exact size of plasmid can be determined by restriction analysis. The cured derivatives of strain NT2 were obtained at a 2% curing efficiency when incubated with ethidium bromide at 40 °C. Curing did not occur when incubated with ethidium bromide at 30 °C or without ethidium bromide at 40 °C. Cured variants failed to grow on MSB agar and lost the ability to utilize 2,4-DNT as a sole source of carbon and energy. Agarose gel electrophoresis confirmed that such cured variants did not harbour plasmid (lane 2). Transformation of E. coli DH5α resulted in subsequent growth of the transformants on MSB agar plates containing 2,4-DNT (0.54 mM). The transformation frequency was 2.0 × 10−6 colonies per donor cell. Agarose gel electrophoresis of plasmid preparation of the transformant revealed the presence of plasmid as that of donor (lane 3). The degradation ability of transformant DH5α and cured strain was tested in MSB containing 2,4-DNT (0.54 mM). Strain NT2 was used as positive control while DH5α was used as negative control. It was observed that only parent strain NT2 and transformant DH5α could utilize 2,4-DNT as a sole source of carbon and energy. This was evident from their estimated 2,4-DNT degradation abilities (Table S7; ESI†). No significant 2,4-DNT degradation was observed in culture broths of non-transformant E. coli DH5α and cured variants (Table S7; ESI†). The analysis of the antibiotic resistance profiles of NT2, competent DH5α transformant revealed that the transfer of antibiotic resistance correlated with the transfer of plasmid as well as 2,4-DNT degrading property (Table S8; ESI†). However, further investigation is essential to draw any definite conclusion.Earlier reports have shown the presence of both small and large plasmid(s) during degradation of 2,4-DNT. For instance, Küce et al.11 reported the possible involvement of plasmid pArK1 (∼8.1 kb) from 2,4-DNT degrading Arthrobacter sp. K1. However, DNT dioxygenase gene in Pseudomonas sp. strain is localized on a large (180 kb) plasmid.68 Similarly, the degradation ability of Rhodococcus genus for wide variety of xenobiotics is also plasmid-borne. These results suggest that the plasmids distributed throughout the actinomycetes play an intriguing role in propagating the nitroaromatics catabolism genes and provide evidence of microbial response to xenobiotics. However, additional work needs to be done in order to clearly understand the genetic basis of 2,4-DNT degradation.
4. Conclusions
This study mainly focused on the kinetics of growth and biodegradation and determination of 2,4-DNT metabolic pathway employed by R. pyridinivorans NT2. In particular, it was able to tolerate and consume 2,4-DNT as sole source of C, N and energy up to 2 mM and its growth kinetics was well characterized by Andrews–Haldane substrate inhibition model. The mechanisms undertaken by strain NT2 (changes in the FAMEs profiles and cell sizes, alternation in enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant defense systems, and accumulation of carotenoids) during growth and degradation of 2,4-DNT may be extended to other rhodococci usually present in resource-limited extreme environments. Increased cell surface hydrophobicity along with glycolipidic biosurfactant production indicated dissolution of 2,4-DNT into aqueous phase followed by interfacial uptake. The degradation intermediates identified for this strain are similar to the metabolites involved in the pathway reported for Pseudomonas species. Interestingly, strain NT2 harbors a catabolic plasmid probably containing genes for 2,4-DNT assimilation. Further studies will contribute to understand the role of the biosurfactant in this organism and to clone and sequence novel catabolic gene(s) to explore its substrate specificities. Given the unique metabolic capabilities and distinctive responses described here, R. pyridinivorans strain NT2 could potentially be exploited either as a potential candidate for bioremediation of the DNTs-contaminated environment or for the bioproduction of high-value carotenoids and glycolipid biosurfactants, from DNTs-containing waste or industrial discharge.Acknowledgements
Debasree Kundu acknowledges Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (C.S.I.R), New Delhi for providing CSIR-SRF fellowship. Chinmay Hazra thanks Department of Science and Technology (D.S.T), New Delhi for providing INSPIRE-SRF fellowship. The authors are also thankful to University Grants Commission (U.G.C), New Delhi and Department of Science and Technology (D.S.T), New Delhi for funding under SAP and FIST program, respectively, to the university.References
- D. Singh and G. Ramanathan, Biodegradation, 2013, 24, 645–655 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. S. Ju and R. E. Parales, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2010, 74, 250–272 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Kulkarni and A. Chaudhari, J. Environ. Manage., 2007, 85, 496–512 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Paca, M. Halecky, T. Hudcova and R. Bajpai, Folia Microbiol., 2008, 53, 105–109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Leungsakul, B. G. Keenan, M. Mori, M. D. Morton, J. D. Stuart, B. F. Smets and T. K. Wood, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2006, 93(2), 231–237 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Jenkins, A. Hewitt, C. Grant, S. Thiboutot, G. Ampleman, M. Walsh, T. Ranney, C. Ramsey, A. Palazzo and J. Pennington, Chemosphere, 2006, 63(8), 1280–1290 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Küce, G. Coral and Ç. Kantar, Ann. Microbiol., 2015, 65, 467–476 CrossRef.
- J. Xu and N. Jing, J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 203–204, 299–307 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Ö. S. Kuşçu and D. T. Sponza, J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 187, 222–234 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Paca, M. Halecky, J. Barta and R. Bajpai, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 163, 848–854 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. H. Keith and W. A. Telliard, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1979, 13, 416–423 CrossRef.
- S. Han, S. T. Mukherji, A. Rice and J. B. Hughes, Chemosphere, 2011, 85, 848–853 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Spanggord, J. C. Spain, S. F. Nishino and K. E. Mortelmans, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1991, 57, 3200–3205 CAS.
- D. L. Freedman and D. R. Noguera, DTIC report, U. S. Army Research Office, NC, 1995 Search PubMed.
- T. Hudcova, M. Halecky, E. Kozliak, M. Stiborova and J. Paca, J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 192, 605–613 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Podlipná, B. Pospíšilová and T. Vaněk, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2015, 112, 54–59 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. L. Kaplan, in Organic Energetic Compounds, ed. P. L. Marinkas, Nova Science Publishers, New York, 1996 Search PubMed.
- B. F. Smets and R. J. Mueller, Biodegradation, 2001, 12, 209–217 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Valli, B. J. Brock, D. K. Joshi and M. H. Gold, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1992, 58(1), 221–228 CAS.
- C. Zhang and G. N. Bennett, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2005, 67(5), 600–618 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. T. Montgomery, R. B. Coffin, T. J. Boyd, J. P. Smith, S. E. Walker and C. L. Osburn, Environ. Pollut., 2011, 159, 3673–3680 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Paca, J. Barta and R. Bajpai, Soil Sediment Contam., 2005, 14, 261–279 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Yang, A. Halasz, J.-S. Zhao, F. Monteil-Rivera and J. Hawari, Chemosphere, 2008, 70, 791–799 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. D. Roldan, E. Pérez-Reinado, F. Castillo and C. Moreno-Vivian, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2008, 32, 474–500 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Kundu, C. Hazra, N. Dandi and A. Chaudhari, Biodegradation, 2013, 24, 775–793 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Kundu, C. Hazra and A. Chaudhari, Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci., 2015, 4(1), 564–574 Search PubMed.
- J. A. Salam and N. Das, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2014, 30, 1301–1313 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Kulkarni and A. Chaudhari, Bioresour. Technol., 2006, 97, 982–988 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. W. Rice, Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, 2001 Search PubMed.
- H. A. C. Montgomery and J. F. Dymock, Analyst, 1961, 86, 414–416 CAS.
- J. Sambrook, E. F. Fritsch and T. Maniatis, Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Coldspring Harbour Laboratory Press, USA, 1989 Search PubMed.
- E. S. Christine, in Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, ed. F. M. Ausbel and R. Brent, John Wiley & Sons Inc., NY, 1994, pp. 1.8.1–1.8.3 Search PubMed.
- B. Gumuscu and T. Tekinay, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2013, 85, 35–41 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. H. Kwon and S. H. Yeom, Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng., 2009, 32, 435–442 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Bajaj, C. Gallert and J. Winter, Biochem. Eng. J., 2009, 46, 205–209 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Shen, R. He, L. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Zuo, Y. Li, X. Sun, J. Li and W. Han, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 167, 193–198 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Banerjee and A. K. Ghoshal, Bioresour. Technol., 2010, 101, 5501–5507 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Shen, X. Zhang, D. Chen, X. Liu, L. Zhang, X. Sun, J. Li, H. Bi and L. Wang, Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng., 2014, 37, 1185–1192 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Surhio, F. N. Talpur, S. M. Nizamani, F. Amin, C. W. Bong, C. W. Lee, M. A. Ashraf and M. R. Shah, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 55960–55966 RSC.
- J. Yan, W. Jianping, L. Hongmei, Y. Suliang and H. Zongding, Biochem. Eng. J., 2005, 24, 243–247 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Basak, B. Bhunia, S. Dutta, S. Chakraborty and A. Dey, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2014, 21, 1444–1454 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Stoilova, A. Krastanov, V. Stanchev, D. Daniel, M. Gerginova and Z. Alexieva, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 2006, 39, 1036–1041 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. A. Wolski, I. Durruty, P. M. Haure and J. F. González, Water, Air, Soil Pollut., 2012, 223, 2323–2332 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Christen, A. Vega, L. Casalot, G. Simon and R. Auria, Biochem. Eng. J., 2012, 62, 56–61 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Shareefdeen, B. C. Baltzis, Y. S. Oh and R. Bartha, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1993, 41(5), 512–524 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. K. Sahoo, K. Pakshirajan and P. K. Ghosh, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2011, 165, 1587–1596 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. K. Singh, S. Kumar, S. Kumar and A. Kumar, Biochem. Eng. J., 2008, 40, 293–303 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Shen, R. He, L. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Zuo, Y. Li, X. Sun, J. Li and W. Han, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 167, 193–198 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. C. C. R. de Carvalho, Res. Microbiol., 2012, 163, 125–136 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Vilcheze, H. R. Morbidoni, T. R. Weisbrod, H. Iwamoto, M. Kuo, J. C. Sacchettini and W. R. Jacobs Jr, J. Bacteriol., 2000, 182, 4059–4067 CrossRef CAS.
- H. M. Alvarez, R. A. Silva and A. C. Cesari, et al., FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2004, 50, 75–86 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, H. Wang and F. Hua, Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip., 2013, 27, 4256–4262 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Hazra, D. Kundu and A. Chaudhari, RSC Adv., 2015, 5(4), 2974–2982 RSC.
- C. Hazra, D. Kundu, P. Ghosh, S. Joshi, N. Dandi and A. Chaudhari, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2011, 86(2), 185–198 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. C. Schmidt, D. Meinzer, L. Kaminski, E. Low and G. Stork, Chromatographia, 1997, 46, 501–505 CAS.
- Y. Yin, Y. Xiao, H.-Z. Liu, F. Hao, S. Rayner, H. Tang and N.-Y. Zhou, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2010, 87, 2077–2085 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. R. Kim, M. K. Kong, S. Y. Lee and P. C. Lee, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2010, 26, 2231–2239 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-T. Zheng, M. Toyofuku, N. Nomura and S. Shigeto, Anal. Chem., 2013, 85, 7295–7301 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. M. Bradley, F. H. Chapelle, J. E. Landmeyer and J. G. Schumacher, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1994, 60, 2170–2175 CAS.
- D. R. Noguera and D. L. Freedman, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1996, 62, 2257–2263 CAS.
- Z.-Y. Wang, Z.-F. Ye and M.-H. Zhang, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2011, 110, 1476–1484 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Huang, G. Ning, F. Li and G. D. Sheng, Bioresour. Technol., 2015, 180, 200–206 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Wicht, Water Sci. Technol., 1996, 34, 99–106 CrossRef CAS.
- M. S. Dueholm, M. Albertsen, S. D'Imperio, V. P. Tale, D. Lewis, P. H. Nielsen and J. L. Nielsen, Genome Announcements, 2014, 2(3), e00525 Search PubMed.
- B. Kriszt, A. Táncsics, M. Cserháti, Á. Tóth, I. Nagy, B. Horváth, I. Nagy, T. Tamura, J. Kukolya and S. Szoboszlay, J. Bacteriol., 2012, 194, 1247–1248 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. L. Gemini, A. Gallego, V. M. de Oliveira, C. E. Gomez, G. P. Manfio and S. E. Korol, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2005, 55, 103–108 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Cassidy, A. Northup and D. Hampton, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2009, 84, 820–826 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. C. Suen and J. C. Spain, J. Bacteriol., 1993, 175, 1831–1837 CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c5ra02450a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |