Identification of nitric oxide-releasing derivatives of oleanolic acid as potential anti-colon cancer agents†
Abstract
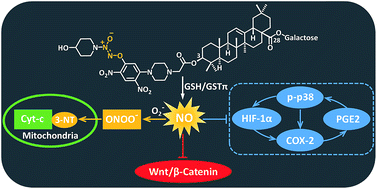
A group of nitric oxide (NO)-releasing derivatives of oleanolic acid (OA) (5–13) were designed, synthesized and biologically evaluated for their anti-colon cancer activity. It was found that the most potent compound 6 preferably released high levels of NO in colon cancer cells but not in normal cells, leading to potent cytotoxicity against colon cancer cells. In addition, 6 was more prone to produce NO catalyzed by GSTπ relative to GSTα. Furthermore, 6 significantly inhibited the tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model. Finally, 6 induced nitration of tyrosine residues in mitochondrial protein, down-regulated Wnt/β-catenin pathway, and inhibited COX-2 centered signaling loop in colon cancer cells. Collectively, our findings suggested that 6 could be a promising candidate for the intervention of colon cancer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...