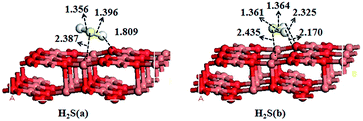DFT study on the adsorption and dissociation of H2S on CuO(111) surface
Shujuan Sun*a,
Dongsheng Zhanga,
Chunyu Lib and
Yanji Wang*a
aSchool of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300130, P. R. China. E-mail: sunshujuan@hebut.edu.cn; yjwang@hebut.edu.cn
bScience and Technology Innovation Center, Datang Technologies Industry Group Company Limited, Beijing 100097, P. R. China
First published on 18th February 2015
Abstract
Density functional theory (DFT) together with periodic slab models is employed to investigate the adsorption and dissociation of H2S on the CuO(111) surface. The structures of H2S, SH, S atom, and H atom on the CuO(111) surface, as well as the co-adsorption of SH and a H atom, and the co-adsorption of S atom and two H atoms, have been determined. The pathways of the dissociation of H2S on the CuO(111) surface are constructed. The activation energy and reaction energy of each step in different pathways are also calculated. The energy barrier of the first dehydrogenation process in the pathway 2 is 0.60 kJ mol−1 higher than that in the pathway 1, but the energy barrier of the second dehydrogenation process in the pathway 2 is 23.50 kJ mol−1 lower than that in the pathway 1, implying that the structure with two H atoms adsorbed on the Osuf sites is the most probable product for the dissociation of H2S on the CuO(111) surface.
1. Introduction
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is one of the most common compounds and can be produced in many industrial processes, such as coal or residual oil gasification, fuel cell applications, ammonia synthesis from hydrocarbon feedstock. It is a highly odorous and toxic substance, and it is the sources of the acid rain when it is oxidized to sulfur oxide and reacted with water. So it must be removed to avoid corrosion and environmental problems. It is well known that, when compared with the conventional wet scrubbing methods, high-temperature desulfurization can substantially improve the thermal efficiency of processes. For the removal of H2S, various kinds of metal oxides have been investigated as solid sorbents, such as Cu2O, ZnO, CeO2, CuO, Fe2O3, Mn2O3 and Co3O4.1–5CuO is known to be used as a highly efficient sorbent to remove H2S,6,7 and various CuO-based sorbents are used to investigate effects of sorbent ingredients.5,8 Thermodynamics suggest that a lower equilibrium H2S level can be achieved with Cu oxide than with Fe and Ca oxides below 800 °C.9 Jiang et al.10 prepared a series of Cu–Zn and Cu–Zn–Al catalysts with varying metal molar ratios. And the results showed that the Cu-rich adsorbents were more suitable for H2S adsorption at the low temperature than the Zn-rich adsorbents, which might be mainly attributed to faster sulfidation rate of the CuO than that of the ZnO. Kyotani et al.11 prepared five kinds of CuO-containing solids, and found that physical mixing of CuO with inert solid was sufficient to increase the reactivity and lifetime of the sorbent.
Density functional theory has been widely used to calculate the adsorption energy, structure parameters, activation energy and reaction energy in the process of different reactions. And molecular modeling and computational investigations have made important contributions towards understanding the adsorption and dissociation of H2S on metal and metal oxide catalysts, such as gold cluster,12 Au(100) surface,13 Fe(110) surface,14,15 Cu2O(111) surface,16 ZnO(10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surface,17 Mo(100) surface.18 In many processes, removal of H2S involves its reaction and dissociation on a surface to form elemental sulfur and hydrogen. The dissociation pathway studied here involves sequential abstraction of H atoms from H2S.19,20 H–S bond cleavage is an essential step in transformation of H2S into elemental sulfur. The following reaction steps are of primary interest:
0) surface,17 Mo(100) surface.18 In many processes, removal of H2S involves its reaction and dissociation on a surface to form elemental sulfur and hydrogen. The dissociation pathway studied here involves sequential abstraction of H atoms from H2S.19,20 H–S bond cleavage is an essential step in transformation of H2S into elemental sulfur. The following reaction steps are of primary interest:
| H2S(ads) → SH(ads) + H(ads) | (1) |
| SH(ads) → H(ads) + S(ads) | (2) |
Although many researches have been devoted to understanding the sulfidation of sorbent, little is known about the adsorption process and dissociation pathways of H2S on CuO. Therefore, a theoretical approach is particularly useful for providing important information on the structure and energetics of H2S adsorption on the CuO. CuO(111) surface is one of the predominant growth surfaces, which has been used in our previous work.21,22 In this paper, the energies of H2S adsorption and dissociation pathway on the CuO(111) surface are investigated to understand the behavior of H2S on CuO(111) surface by density functional theory. The reaction barrier of each elementary step from H2S to S and two H has been investigated. The aim of this work is to provide a better understanding of the dissociation mechanism of H2S on the CuO(111) surface.
2. Computational model and method
2.1 Computational model
Previous studies have shown that CuO(111) have the lower surface free energy,23 and the low surface energy structure is the most stable under realistic conditions.16 The adsorption properties of CuO(111) is investigated using the supercell approach.21,22 Periodic boundary condition is applied to the central supercell so that it is reproduced periodicity throughout the whole calculation space. Fig. 1 displays the top view of CuO(111) surface configurations. The CuO(111) surface includes eight different types of surface adsorption sites, including “Cusuf”, “Cusub”, “Osuf”, “Osub”, “Cusub–Cusub bridge”, “Osub–Osub bridge”, “Osuf–Osuf bridge”, “Cusuf–Cusuf bridge” sites, which are denoted as I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII and VIII, respectively. The Cusuf (I) is the outer-most surface copper atom and the Cusub (II) is the subsurface copper atom. The Osuf (III) is the outer-most oxygen atom and the Osub (IV) is the subsurface oxygen atom.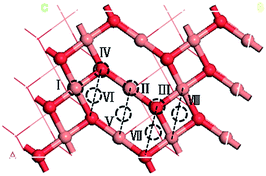 | ||
| Fig. 1 The top view of the CuO(111) surface. The orange and red spheres represent the Cu and O atoms, respectively. | ||
A six-layer slab with a [3 × 2] unit cell is used to model the 1/6 monolayer (ML) coverage. The unit cell of the CuO(111) surface consists of 24 distinct Cu atoms and 24 distinct O atoms. Adsorbate and the top tree atomic layers of the substrate are allowed to relax in all of the geometry optimization calculations. The vacuum region between slabs is 10 Å to eliminate spurious interactions between the adsorbate and the periodic image of the bottom layer of the surface.24
2.2 Computational method
The density functional theory calculation has been carried out by Dmol3 program package in Materials Studio 7.1.25,26 The main calculations are based on the generalized gradient approximation with a PW91 exchange-correction function.27,28 It is important to point out that the commonly used DFT exchange correlation functional tend to underestimate adsorption energies because formally they do not take into consideration van der Waals (vdW) dispersion forces.29 The DFT calculations coupled with a van der Waals-inclusive correction (DFT-D) are carried out to improve the calculations.30,31 The valence electron functions were expanded into a set of numerical atomic orbitals by a double numerical basis with polarization functions (DNP). In the computation, the inner electrons of copper atom are kept frozen and replaced by an effective core potential (ECP),32 and other atoms in this study are treated with an all electron basis set.A Monkhorst–Pack mesh k-points grid of 3 × 2 × 2 is used to simplify the Brillouin zone and the real space cutoff radius is maintained as 5.0 Å. The parameters criteria for the tolerances of energy, force, displacement, and SCF convergence criteria are 1.0 × 10−5 Ha, 0.002 Ha Å−1, 0.005 Å, and 1.0 × 10−6, respectively. A Methfessel–Paxton smearing of 0.005 Ha is used to improve calculation performance. Meanwhile, transition state (TS) search is performed at the same theoretical level with the complete linear synchronous transit and quadratic synchronous transit (LST/QST) method.24,33,34
The adsorption energy is regard as a measure of the strength of adsorbate–substrate adsorption. The adsorption energy of all adsorbed molecule is calculated according to the following formula:
| Eads = Eadsorbate + ECuO(111) − Eadsorbate/CuO(111) |
2.3 The size effect of surface on calculation
To investigate the necessary size for surface, the adsorption energies and Mulliken charges for H2S adsorbed at Cusub site with S-down are compared for different supercell, which are shown in Table 1. As can be seen from Table 1, the adsorption energies have a relatively large change from the 1/2 to 1/6 ML coverage. And the similar adsorption energies are obtained from the 1/6 and 1/9 ML coverage. Hence, a [3 × 2] supercell is employed in the study.3. Results and discussion
To validate the reliability of calculation methods, the bulk lattice parameters for CuO are calculated. CuO has a monoclinic structure with space group C2/c1 (a = 4.683 Å, b = 3.422 Å, c = 5.129 Å and β = 99.54°).35 The calculated structural parameters (Cu–O bond lengths: 1.971 Å, 1.969 Å; and O–Cu–O angle = 83.3°) are in good agreement with the experimental results and other calculated date.36,37 Meanwhile, as summarized in Table 1, the calculated geometrical parameters, and vibrational frequencies of gas-phase H2S are in line with available experimental38 and theoretical dates.16 As shown in Table 2, The GGA-PW91 functional provides the best overall results. In addition, in the previous study, the GGA-PW91 functional is used to calculate the mercury adsorption on the CuO surface.22,39 Therefore, the GGA-PW91 functional is used in the following calculations.3.1 H2S adsorption on the CuO(111) surface
As to the adsorption of H2S, three types of initial configurations of H2S molecule reacting with the adsorption sites are examined: (1) H2S is perpendicular to the surface with S binding to the adsorption sites; (2) H2S tilts to the surface so that one H atom is parallel to the adsorption sites; (3) H2S is parallel to the surface with S binding to the adsorption sites. After optimization, most of the adsorption energies are about 40 kJ mol−1 and only two adsorption energies are above 70 kJ mol−1, which are shown in Fig. 2 and the adsorption energies are listed in Table 3. Here, only the two stable adsorption configurations are considered.| Model | Eads/kJ mol−1 | Model | Eads/kJ mol−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2S(a) | 79.04 | SH(a) | 187.24 |
| H2S(b) | 73.81 | SH(b) | 190.07 |
| H(a) | 168.06 | SH(c) | 61.75 |
| H(b) | 177.41 | SH(d) | 159.24 |
| H(c) | 324.78 | S | 217.35 |
| H(d) | 75.82 |
As shown in Fig. 2, H2S is adsorbed at Cusub site as a molecule. In H2S(a), one of the H atom is adsorbed at Osuf site with a distance of 1.809 Å. And in H2S(b), the two H atoms are all adsorbed at Osuf sites with distance of 2.170 and 2.325 Å, respectively. The adsorption energies of H2S (a) and H2S (b) are 79.04 and 73.81 kJ mol−1, respectively. The adsorption energy is similar to the case of H2S on α-Fe2O3(0001) surface (71.0 kJ mol−1),34 Ir(111) surface40 (74.3 kJ mol−1), Ni(100) surface41 (70.5 kJ mol−1) and Nb-doped Pd surface42 (77.48 kJ mol−1). Evidences for the physical adsorption of H2S on oxide surfaces are seen in studies of H2S on MgO(100) surface, Cr2O3(0001) surface,43,44 Ag(100) surface,45 UO2(001) surface46 and Au(100) surface.13 However, the dissociative adsorption of H2S occurs predominantly on the ZnO(10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surface24 and Si(001) surface.47
0) surface24 and Si(001) surface.47
3.2 SH adsorption on the CuO(111) surface
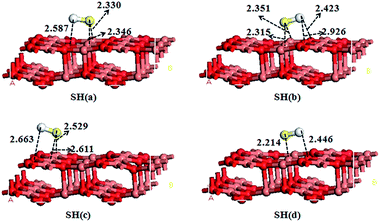
For the adsorption of SH on CuO(111) surface, three molecular orientations, S-down, H-down and SH parallel to the surface, on the all adsorption sites of the CuO(111) surface are examined. During a full optimization, four adsorption modes are obtained displayed in Fig. 3. In SH(a) model, S atom is bonded to two Cusub atoms via the bridge bond and H atom is toward to the Osub atom. The two S–Cu bonds are 2.330 and 2.346 Å in length, respectively, and the adsorption energy is 187.24 kJ mol−1. In SH(b) model, the S atom is also bonded to two Cusub atoms via the bridge bond, but the H atom is toward to two Osuf atoms with the distance of 2.432 and 2.926 Å, respectively. The adsorption energy of SH(b) is 190.07 kJ mol−1. The adsorption energy of SH(c) is 61.75 kJ mol−1, which indicates weak chemisorptions. In SH(d), S atom is bonded to the Cusub atom and H atom is bonded to the Osuf atom. The adsorption energy of SH(d) is 159.24 kJ mol−1. From the adsorption energy, it is indicated that SH(a) and SH(b) are the stable adsorption configurations with S atom bonded to two Cusub atoms via the bridge bond. It is similar to the SH on ZnO(10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surface,24 Pd(111) surface48 and Ni(111) surface.40
0) surface,24 Pd(111) surface48 and Ni(111) surface.40
3.3 S adsorption on the CuO(111) surface
The S atom adsorption on the CuO(111) surface for the most stable adsorption models is obtained after a full optimization, as shown in Fig. 4. The models S bonded to other sites are all converted to the model S bonded to the bridge of two Cusub atoms, with the adsorption energy of 217.35 kJ mol−1. The S atom is bonded to two Cusub atoms via the bridge bond. The bonds of S–Cusub are 2.246 and 2.254 Å in length, respectively.3.4 H adsorption on the CuO(111) surface
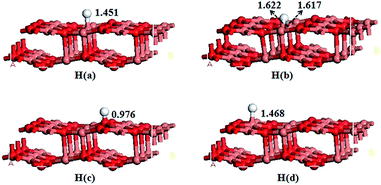
For H adsorption, we considered the models H bonded on all the adsorption sites on the CuO(111) surface and four models are obtained after a full optimization shown in Fig. 5. The adsorption energies are listed in Table 3. As can be seen from the adsorption energy, the H(c) model is the most stable configuration with the adsorption energy of 324.78 kJ mol−1. In H(a), H atom is adsorbed at the Cusub atom with the distance of 1.451 Å. In H(b), H atom is adsorbed at two Cusub atoms via the bridge bond with the distance of 1.622 and 1.617 Å, respectively. In H(c), H atom is adsorbed at the Osuf atom with the distance of 0.976 Å. In H(d), H atom is adsorbed at the Cusuf atom with the distance of 1.468 Å. The adsorption energies of the four models are in the following order: H(c) > H(b) > H(a) > H(d). It is indicated that the Osuf site is found to be the stable site for H adsorption on CuO(111) surface, which is similar to H adsorption on CeO2 (ref. 49) and ZnO.24 However, the metal site is the most stable adsorption site for H adsorption on Cu2O(111) surface.503.5 The co-adsorption of SH and H or S and two H on the CuO(111) surface
To characterize probable reaction pathways of the H2S decomposition processes on the CuO(111) surface, the co-adsorption of SH and a H atom, a S atom and two H atoms, are considered. The co-adsorption structure of SH and H atom is built according to the most stable single adsorptions of SH and H on the CuO(111) surface.34 As above mentioned, three stable adsorption structures of SH on the CuO(111) surface are obtained, which are shown as SH(a), SH(b) and SH(c). Based on these three configurations and the adsorption configurations of H2S on CuO(111) surface, the co-adsorption configurations of SH fragment and a H atom on the CuO(111) surface are investigated, which are shown as IM1 and IM2 in Fig. 6. In the two co-adsorption configures, the S atom is bonded to two Cusub atoms via the bridge bond and the H atom is bonded to the Osuf adsorption site. However, in IM1 the H atom of SH is toward to Osub site with distance of 2.572 Å, and in IM2 the H atom of SH is toward to Osuf site with distance of 2.402 Å. The adsorption energies of IM1 and IM2 are 494.09 and 516.83 kJ mol−1, respectively.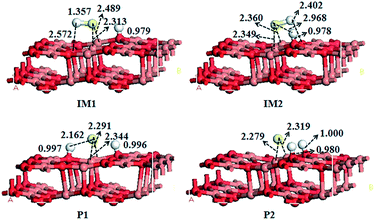 | ||
| Fig. 6 The optimized geometric structures of co-adsorbed of SH and a H atom, a S atom and two H atoms on the CuO(111) surface. | ||
The co-adsorption structures of a S atom and two H atoms are also investigated, see P1 and P2 Fig. 6. In the two co-adsorption configures, the S atom is bonded to two Cusub atoms via the bridge bond. In P1 the H atoms are bonded to Osuf and Osub sites with the distance of 0.996 and 0.997 Å, respectively. However, in P2 the two H atoms are bonded to Osuf sites with the distances of 0.980 and 1.000 Å, respectively. The adsorption energies of P1 and P2 are 861.45 and 884.82 kJ mol−1, respectively.
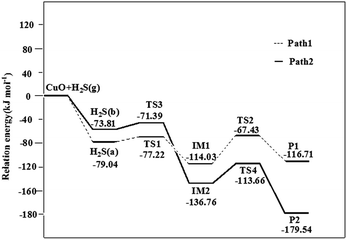
3.6 The dissociation process of H2S on the CuO(111) surface
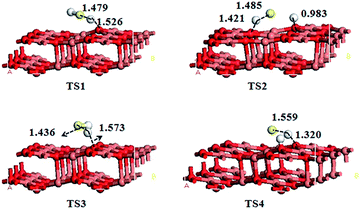
To characterize the dissociation process of H2S on CuO(111) surface, H2S(a) and H2S(b) models are choose as the initial states and the co-adsorption configurations of SH and H are choose as the intermediates. The P1 and P2 configurations are served as final states. The transition states are searched from initial states to intermediates, and intermediates to final states. The structures and bond lengths for the transition states are displayed in Fig. 7. The calculated reaction pathways for H2S dissociated process on CuO(111) surface are presented in Fig. 8.As can be seen from the Fig. 2, in H2S(a) model, one H atom bounds to Osuf atom and another H atom is inclined to adsorb at Osub atom. In H2S(b) model, the two H atoms all bound to Osuf atoms. According to the adsorption sites of H atoms in IM1 and IM2 models in Fig. 6, two pathways (H2S(a) → IM1 → P1, H2S(b) → IM2 → P2) are formed. For pathway 1, H2S(a) configuration is choose as the reactant. H2S initially adsorbs on the surface with an adsorption energy of 79.04 kJ mol−1. Then, the first dehydrogenation process (H2S → SH + H) happens and the dissociating H atom diffuses into the adjacent surface Osuf atom and forms an O–H bond via TS1 with an energy barrier of 1.82 kJ mol−1. The distances between the dissociative H atom and the S atom, Osuf atom on the surface are 1.479 and 1.526 Å, respectively. This step is an exothermic process with the formation of intermediate IM1 and the reaction energy of 34.99 kJ mol−1. Subsequently, the second dehydrogenation step (SH → S + H) takes place by overcoming an energy barrier of 46.60 kJ mol−1 at TS2 and leads to the formation of P1 with a reaction energy of 2.68 kJ mol−1. In the structure of TS2, the lengths of the breaking S–H and forming Osub–H bonds are 1.485 and 1.421 Å, respectively.
For the pathway 2, the H2S(b) configuration is choose as the reactant and the adsorption energy of H2S(b) is 73.81 kJ mol−1. As the H2S molecule comes apart, the SH fragment tilts toward the surface and ends in a bridge configuration with the S atom with an energy barrier of 2.42 kJ mol−1 in the first dehydrogenation step. In TS3, both SH and H are close to adjacent Osuf sites, with the dissociating H 1.436 Å away from the S atom of the SH fragment. The values are increased by 0.075 Å compared to the molecularly adsorbed H2S(H2S(b)). For the second dehydrogenation step, this step is an exothermic process with the formation of product P2 and the reaction energy of 42.78 kJ mol−1. The energy barrier is 23.10 kJ mol−1. In TS4, the SH bond is broken, and the distance between S and H is 1.559 Å. The H atom dissociated from the SH is close to the Osuf site with the distance of 1.320 Å.
According to the calculation of pathway 1 and pathway 2, the first dehydrogenation process can easily take place with a small energy barrier of 1.82 and 2.42 kJ mol−1, respectively, to overcome. The low energy barriers reveal that adsorbed H2S is unstable on the CuO(111) surface. However, H2S weakly molecularly bonded to the CeO2(111) surface need to overcome little energy barrier of 7.95 kJ mol−1 for the first dehydrogenation by the DFT calculation.49 For the second dehydrogenation process, the energy barrier of pathway 2 is 23.10 kJ mol−1, which is 23.50 kJ mol−1 smaller than that of pathway 1. From the energy barrier of the second dehydrogenation process, it is concluded that pathway 2 is the most probable reaction process for the H2S dissociation on the CuO(111) surface. The barriers for the first and second dehydrogenation process are about 9.65, 0 kJ mol−1 on Fe(110),14 35.70, 3.86 kJ mol−1 on Pd (111) surface,19 35.66, 51.47 kJ mol−1 on ZnO(10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surface,24 and 52.4, 82.7 kJ mol−1 on Cu2O(111) surface. It is concluded that CuO(111) surface exhibits a strong catalytic activity toward the dissociation of H2S.
0) surface,24 and 52.4, 82.7 kJ mol−1 on Cu2O(111) surface. It is concluded that CuO(111) surface exhibits a strong catalytic activity toward the dissociation of H2S.
4. Conclusion
The adsorption and decomposition mechanism of H2S on the CuO(111) surface have been investigated using density functional theory together with periodic slab models. The most stable adsorption structures and adsorption energies for H2S, SH, S and H species, as well as the coadsorption of SH fragment and a H atom, and of a S atom and two H atoms are identified. The results show that H2S is adsorbed on the CuO(111) surface with S atom bonded on Cusub site. It is proposed that the most stable configurations for SH and S on the CuO(111) surface is the S atom is bonded to two Cusub atoms via the bridge bond, where as H adsorb preferentially on the Osuf site. The energy barrier for the dissociation of H2S is obtained. The pathway for the two H atoms adsorbed on Osuf sites is the probable reaction process. In the pathway, the energy barriers of the first and second dehydrogenation process are 2.42 and 23.10 kJ mol−1, respectively, which indicated that CuO(111) surface exhibits a strong catalytic activity toward the dissociation of H2S.Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21236001, 21106029), National Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (12JCQNJC03000) and National Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (B2012202043).References
- J. Lin, J. A. May, S. V. Didziulis and E. I. Solomon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114, 4718–4727 CrossRef CAS.
- T.-H. Ko, H. Chu and L.-K. Chaung, Chemosphere, 2005, 58, 467–474 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Alonso, J. M. Palacios, E. García and R. Moliner, Fuel Process. Technol., 2000, 62, 31–44 CrossRef CAS.
- H. No'man, E.-B. Ribhi and A.-W. Abdulrakib, Desalination, 2005, 181, 145–152 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Montes, E. Tocuyo, E. González, D. Rodríguez, R. Solano, R. Atencio, M. A. Ramos and A. Moronta, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2013, 168, 111–120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Park, S. Park, J. Jung, T. Hong, S. Lee, H. W. Kim and C. Lee, Ceram. Int., 2014, 40, 11051–11056 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Laperdrix, G. Costentin, O. Saur, J. C. Lavalley, C. Nédez, S. Savin-Poncet and J. Nougayrédez, J. Catal., 2000, 189, 63–69 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. K. Song, K. B. Lee, H. S. lee and Y. W. Rhee, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 2000, 17, 691–695 CrossRef CAS.
- P. R. Westmoreland and D. P. Harrison, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1976, 10, 659–661 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Jiang, L. Su, L. Ma, N. Yao, X. Xu, H. Tang and X. Li, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2010, 256, 3216–3223 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Kyotani, H. Kawashima and A. Tomita, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1989, 23, 218–223 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Kuang, X. Wang and G. Liu, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257, 6546–6553 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Jiang, M. Li, P. Qin and T. Fang, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 311, 40–46 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. E. Jiang and E. A. Carter, Surf. Sci., 2005, 583, 60–68 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. E. Jiang and E. A. Carter, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 19140–19145 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Zhang, H. Liu, J. Li, L. Ling and B. Wang, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2012, 258, 9932–9943 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Ling, J. Wu, J. Song, P. Han and B. Wang, Comput. Theor. Chem., 2012, 1000, 26–32 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Luo, J. Cai, X. Tao and M. Tan, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 292, 328–335 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. R. Alfonso, A. V. Cugini and D. C. Sorescu, Catal. Today, 2005, 99, 315–322 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Ren, X. Wang, Y. Miao, L. Yi, X. Jin and Y. Tan, J. Mol. Struct.: THEOCHEM, 2010, 949, 96–100 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sun, Y. Wang and Q. Yang, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 313, 777–783 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sun, D. Zhang, C. Li, Y. Wang and Q. Yang, Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 258, 128–135 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Hu, D. Li, J. G. Lu and R. Wu, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 17120–17126 CAS.
- L. Ling, R. Zhang, P. Han and B. Wang, Fuel Process. Technol., 2013, 106, 222–230 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Delley, J. Chem. Phys., 1990, 92, 508–517 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Delley, J. Chem. Phys., 2000, 113, 7756–7764 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Perdew, K. Burke and M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77, 3865–3868 CrossRef CAS.
- J. P. Perdew and Y. Wang, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1992, 45, 13244–13249 CrossRef.
- M. Callsen, N. Atodiresei, V. Caciuc and S. Blügel, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 2012, 86, 085439 CrossRef.
- F. Ortmann and F. Bechstedt, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 2006, 73, 205101 CrossRef.
- P. Sony, P. Puschnig, D. Nabok and C. Ambrosch-Draxl, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2007, 99, 176401 CrossRef.
- M. Dolg, U. Wedig, H. Stoll and H. Preuss, J. Chem. Phys., 1987, 86, 866–872 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. A. Halgren and W. N. Lipscomb, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1977, 49, 225–232 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Song, X. Niu, L. Ling and B. Wang, Fuel Process. Technol., 2013, 115, 26–33 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Åsbrink and L. J. Norrby, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem., 1970, 26, 8–15 CrossRef.
- Y. Maimaiti, M. Nolan and S. D. Elliott, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16, 3036–3046 RSC.
- J. L. V. Moreno, A. A. B. Padama and H. Kasai, CrystEngComm, 2014, 16, 2260–2265 RSC.
- G. Herzberg, Molecular spectra and molecular structure electronic spectra and electronic structure of polyatomic molecules, Krieger, Malabar, FL, 1966, vol. III Search PubMed.
- W. Xiang, J. Liu, M. Chang and C. Zheng, Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 200–202, 91–96 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. R. Alfonso, Surf. Sci., 2008, 602, 2758–2768 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Hernandez, D.-H. Lim, H. V. P. Nguyen, S.-P. Yoon, J. Han, S. W. Nam, C. W. Yoon, S.-K. Kim and H. C. Ham, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39, 12251–12258 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Ozdogan and J. Wilcox, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2010, 114, 12851–12858 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. A. Rodriguez, T. Jirsak, M. Pérez, S. Chaturvedi, M. Kuhn, L. González and A. Maiti, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122, 12362–12370 CrossRef CAS.
- J. A. Rodriguez, T. Jirsak and S. Chaturvedi, J. Chem. Phys., 1999, 111, 8077–8087 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Qin and J. L. Whitten, Surf. Sci., 2005, 588, 83–91 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Wu, B. V. Yakshinskiy and T. E. Madey, Surf. Sci., 2003, 523, 1–11 CrossRef CAS.
- M. C. Akmak and G. P. Srivastava, Surf. Sci., 1999, 433–435, 420–424 Search PubMed.
- M. P. Hyman, B. T. Loveless and J. W. Medlin, Surf. Sci., 2007, 601, 5382–5393 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-T. Chen, Y. Choi, M. Liu and M. C. Lin, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 11117–11122 CAS.
- R. Zhang, H. Liu, L. Ling, Z. Li and B. Wang, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257, 4232–4238 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |