Oxygen adsorption properties on a palladium promoted La1−xSrxMnO3 solid oxide fuel cell cathode
Abstract
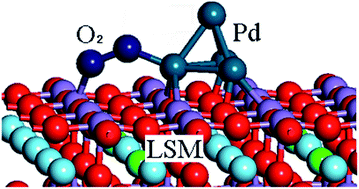
Surface reactions of O2 molecules on a Sr-doped LaMnO3 (LSM) cathode and Pd impregnated LSM cathode are investigated by the first principles method. A tetrahedral Pd4 cluster is used to simulate the Pd particles on the LSM surface. The calculated adsorption energies demonstrate that the pre-adsorbed Pd facilitates O2 adsorption on the surface. The bond length of adsorbed O2 species and corresponding dissociation energies indicate that O2 molecules on the Pd/LSM cathode surface can be dissociated more easily than on the pure LSM surface. The pre-adsorbed Pd (atom and cluster) can serve as an active center on the surface and enhance the electron transference properties during the oxygen reduction reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...