Sorption of atrazine, alachlor and trifluralin from water onto different geosorbents
Abstract
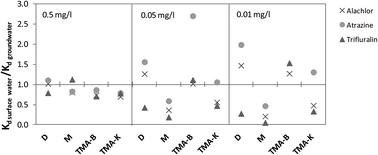
The sorption behavior of the herbicides atrazine, alachlor and trifluralin on four sorbents (two modified organoclays, one model sediment, and one natural sediment) in three water matrices (synthetic water, natural groundwater and surface water) was investigated. The influence of the sorbent and water matrix characteristics was elucidated. All adsorption isotherms fitted well with the Freundlich model. Based on the Kd values, the organically modified bentonite and model sediment proved to be the most effective sorbents for the investigated herbicides. A linear correlation of Kd with the total organic carbon (TOC) concentration was found for trifluralin in the synthetic water matrix (c0 = 0.01 mg L−1). In the case of higher trifluralin concentration and for other tested herbicides at all concentrations the influence of both the sorbent organic matter quality and possible interactions with the mineral phase was indicated. Furthermore, the results showed different influence of the type and the content of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in the water phase on the sorption of all the herbicides, depending on the herbicide concentration and the sorbent applied. It was confirmed that the comparison of sorbent efficiency should be done in native matrix since sorption coefficients vary depending on pollutant concentration, DOC concentration and DOC fraction. This finding is considered to be important for remediation of contaminated sites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...