Environmentally benign synthesis of saturated and unsaturated aliphatic polyesters via enzymatic polymerization of biobased monomers derived from renewable resources†
Abstract
Aliphatic polyesters are of great interest due to their broad potential applications and sustainability. Itaconate-based aliphatic polyesters are even more appealing in biomedical and pharmaceutical fields, as they are renewable functional polymers that can be biodegradable, biocompatible, and photo-curable, and might be bioresorbable. Herein, various biobased saturated aliphatic polyesters and itaconate-based unsaturated aliphatic polyesters are successfully produced via Candida antarctica Lipase B (CALB)-catalyzed polycondensation of (potentially) biobased dimethyl itaconate, 1,4-butanediol and various diacid ethyl esters, using a two-stage method in diphenyl ether. The synthetic aliphatic polyesters reach high 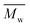 (weight average molecular weight) values up to 94 kg mol−1. Studies on the effect of diacid ethyl esters on the enzymatic polymerization reveal that CALB prefers diacid ethyl esters having a chain length of more than 2 (n > 2, n is the number of methylene groups between the two carbonyl groups); and CALB shows the highest specificity for diethyl adipate among the tested diacid ethyl esters (n = 2–10). Moreover, the structure–property relationships are discussed by investigating the chemical structures, crystalline properties and thermal properties of the obtained aliphatic polyesters, as well as, the thermal transitions and mechanical properties of the UV cross-linked unsaturated polyesters.
(weight average molecular weight) values up to 94 kg mol−1. Studies on the effect of diacid ethyl esters on the enzymatic polymerization reveal that CALB prefers diacid ethyl esters having a chain length of more than 2 (n > 2, n is the number of methylene groups between the two carbonyl groups); and CALB shows the highest specificity for diethyl adipate among the tested diacid ethyl esters (n = 2–10). Moreover, the structure–property relationships are discussed by investigating the chemical structures, crystalline properties and thermal properties of the obtained aliphatic polyesters, as well as, the thermal transitions and mechanical properties of the UV cross-linked unsaturated polyesters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...