Light-dependent activation of G proteins by two isoforms of chicken melanopsins†
Abstract
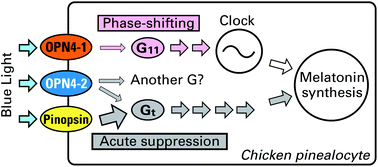
In the chicken pineal gland, light stimuli trigger signaling pathways mediated by two different subtypes, Gt and G11. These G proteins may be activated by any of the three major pineal opsins, pinopsin, OPN4-1 and OPN4-2, but biochemical evidence for the coupling has been missing except for functional coupling between pinopsin and Gt. Here we investigated the relative expression levels and the functional difference among the three pineal opsins. In the chicken pineal gland, the pinopsin mRNA level was significantly more abundant than the others, of which the OPN4-2 mRNA level was higher than that of OPN4-1. In G protein activation assays, Gt was strongly activated by pinopsin in a light-dependent manner, being consistent with previous studies, and weakly activated by OPN4-2. Unexpectedly, illuminated OPN4-2 more efficiently activated G protein(s) that was endogenously expressed in HEK293T cells in culture. On the other hand, Gq, the closest analogue of G11, was activated only by OPN4-1 although the activity was relatively weak under these conditions. These results suggest that OPN4-1 and OPN4-2 couple with Gq and Gt, respectively. Two melanopsins, OPN4-1 and OPN4-2, appear to have acquired mutually different functions through the evolution.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 16th International Conference on Retinal Proteins

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...