Nanoparticle cluster gas sensor: Pt activated SnO2 nanoparticles for NH3 detection with ultrahigh sensitivity†
Abstract
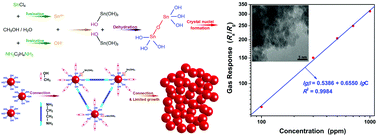
Pt activated SnO2 nanoparticle clusters were synthesized by a simple solvothermal method. The structure, morphology, chemical state and specific surface area were analyzed by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and N2-sorption studies, respectively. The SnO2 nanoparticle cluster matrix consists of tens of thousands of SnO2 nanoparticles with an ultra-small grain size estimated to be 3.0 nm. And there are abundant random-packed wormhole-like pores, caused by the inter-connection of the SnO2 nanoparticles, throughout each cluster. The platinum element is present in two forms including metal (Pt) and tetravalent metal oxide (PtO2) in the Pt activated SnO2 nanoparticle clusters. The as-synthesized pure and Pt activated SnO2 nanoparticle clusters were used to fabricate gas sensor devices. It was found that the gas response toward 500 ppm of ammonia was improved from 6.48 to 203.44 through the activation by Pt. And the results indicate that the sensor based on Pt activated SnO2 not only has ultrahigh sensitivity but also possesses good response–recovery properties, linear dependence, repeatability, selectivity and long-term stability, demonstrating the potential to use Pt activated SnO2 nanoparticle clusters as ammonia gas sensors. At the same time, the formation mechanisms of the unique nanoparticle clusters and highly enhanced sensitivity are also discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editor’s Choice: Making sense of nanosensors and devices

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...