Core–shell Co@Co3O4 nanoparticle-embedded bamboo-like nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes (BNCNTs) as a highly active electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction†
Abstract
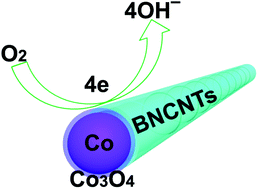
The current bottleneck for fuel cells and metal-air batteries lies in the sluggish oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) on the cathode side. Despite tremendous efforts, to develop a highly efficient ORR catalyst at low cost remains a great challenge. Herein, we have synthesized core–shell Co@Co3O4 nanoparticles embedded in the bamboo-like N-doped carbon tubes (BNCNTs) by a simple approach comprising thermal treatment of cobalt carbonate hydroxide and urea and oxidization. The ORR catalytic activities of the Co@Co3O4/BNCNT composites are closely dependent on the oxidization degree of the Co nanoparticles and the N content in the BNCNTs. When oxidized at 300 °C, the as-formed Co@Co3O4/BNCNTs-300 composite catalyst with an N/C molar ratio of ∼1.6% achieves the maximum ORR catalytic activity. The composite catalyst also exhibits a higher ORR catalytic activity than the Co3O4/carbon nanotube (CNT) catalyst. The tolerance for methanol molecules and the cycle stability performance of the composite catalyst are even superior to those of the highly efficient Pt/C catalyst. Such an excellent ORR catalytic activity can be ascribed to (1) the core–shell Co@Co3O4 nanoparticles embedded in BNCNTs, (2) the N-doping in BNCNTs, and (3) the synergetic effect of (1) and (2) on Co3O4 firmly attached to both Co nanoparticles and BNCNTs, resulting in accelerated electron transport and enhanced charge delocalization.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Graphene-based Energy Devices

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...