A highly efficient non-enzymatic glucose biosensor based on a nanostructured NiTiO3/NiO material
Abstract
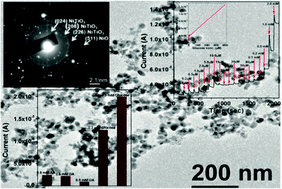
An efficient and novel non-enzymatic glucose sensing platform composed of self-assembled crystalline NiTiO3/NiO nanoparticles is reported in this article. The mixed oxide nanoparticles have been synthesized using a facile sol–gel method mediated by evaporation induced self-assembly (EISA) in non-aqueous media. After annealing at 673 K the final product obtained was well characterized using various analytical tools like powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM), along with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS)and UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) studies which reveal that the nanomaterial is composed of ca. 30–35 nm sized nanocrystals that have an ilmenite NiTiO3 structural phase with some percentage of bunsenite NiO. The NiTiO3/NiO nanoparticles exhibit an outstanding electro-catalytic activity towards glucose oxidation in 0.1 M NaOH alkaline media at an applied potential of +0.55 V (vs. Ag/AgCl electrode). The glucose sensing investigation of this Ni–Ti electrode indicates a very high sensitivity and a low limit of detection (LOD) of 1454 μA mM−1 cm−2 and 0.06 μM, respectively. The glucose level in human blood serum was also tested with our sample which produced a satisfactory result. Thus, the NiTiO3/NiO electrode can be used as a highly effective, economical, stable and non-air sensitive platform for non-enzymatic glucose detection.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...