Evaluation of malonic acid diamide analogues as radical scavenging agents
Abstract
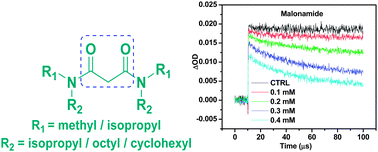
The malonic acid diamide analogues such as N,N′-dimethyl-N,N′-dioctyl-malonamide (DMDOMA), N,N′-dimethyl-N,N′-dioctyl-2,(2′-hexyloxyethyl) malonamide (DMDOHEMA), N,N′-dimethyl-N,N′-dicyclohexyl-malonamide (DMDCMA) and N,N,N′,N′-tetraisopropyl malonamide (TiPMA) were synthesized by an ester amine coupling method. These synthesized diamides were evaluated for the scavenging activity of the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical, superoxide anion scavenging and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), by biochemical methods. Antioxidant properties exhibited by these diamides were compared with standard antioxidants like gallic acid and ascorbic acid. The pulse radiolysis technique was employed to generate 2-2′-azinobis 3-ethylbenzothioline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS˙+), hydroxyl radicals (˙OH), and carbonate (CO3˙−) radicals for evaluating the scavenging activity of the diamides. DMDCMA, TiPMA, and DMDOMA were found to show better antioxidant potential as compared to DMDOHEMA due to their more hydrophilic nature. The pulse radiolysis technique was found to be advantageous for investigating the interaction of the diamide class of compounds with radicals generated under high energy radiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...