Molecular recognition features (MoRFs) in three domains of life†
Abstract
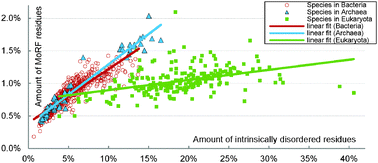
Intrinsically disordered proteins and protein regions offer numerous advantages in the context of protein–protein interactions when compared to the structured proteins and domains. These advantages include ability to interact with multiple partners, to fold into different conformations when bound to different partners, and to undergo disorder-to-order transitions concomitant with their functional activity. Molecular recognition features (MoRFs) are widespread elements located in disordered regions that undergo disorder-to-order transition upon binding to their protein partners. We characterize abundance, composition, and functions of MoRFs and their association with the disordered regions across 868 species spread across Eukaryota, Bacteria and Archaea. We found that although disorder is substantially elevated in Eukaryota, MoRFs have similar abundance and amino acid composition across the three domains of life. The abundance of MoRFs is highly correlated with the amount of intrinsic disorder in Bacteria and Archaea but only modestly correlated in Eukaryota. Proteins with MoRFs have significantly more disorder and MoRFs are present in many disordered regions, with Eukaryota having more MoRF-free disordered regions. MoRF-containing proteins are enriched in the ribosome, nucleus, nucleolus and microtubule and are involved in translation, protein transport, protein folding, and interactions with DNAs. Our insights into the nature and function of MoRFs enhance our understanding of the mechanisms underlying the disorder-to-order transition and protein–protein recognition and interactions. The fMoRFpred method that we used to annotate MoRFs is available at http://biomine.ece.ualberta.ca/fMoRFpred/.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...