Cell-sized condensed collagen microparticles for preparing microengineered composite spheroids of primary hepatocytes
Abstract
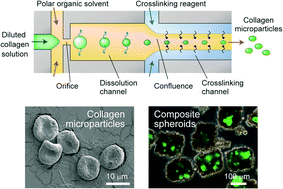
The reconstitution of extracellular matrix (ECM) components in three-dimensional (3D) cell culture environments with microscale precision is a challenging issue. ECM microparticles would potentially be useful as solid particulate scaffolds that can be incorporated into 3D cellular constructs, but technologies for transforming ECM proteins into cell-sized stable particles are currently lacking. Here, we describe new processes to produce highly condensed collagen microparticles by means of droplet microfluidics or membrane emulsification. Droplets of an aqueous solution of type I collagen were formed in a continuous phase of polar organic solvent followed by rapid dissolution of water molecules into the continuous phase because the droplets were in a non-equilibrium state. We obtained highly unique, disc-shaped condensed collagen microparticles with a final collagen concentration above 10% and examined factors affecting particle size and morphology. After testing the cell-adhesion properties on the collagen microparticles, composite multicellular spheroids comprising the particles and primary rat hepatocytes were formed using microfabricated hydrogel chambers. We found that the ratio of the cells and particles is critical in terms of improvement of hepatic functions in the composite spheroids. The presented methodology for incorporating particulate-form ECM components in multicellular spheroids would be advantageous because of the biochemical similarity with the microenvironments in vivo.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...