Abstract
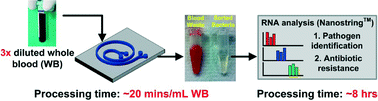
Detection of bacteria in bloodstream infections and their antibiotic susceptibility patterns is critical to guide therapeutic decision-making for optimal patient care. Current culture-based assays are too slow (>48 h), leading to excessive up-front use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and/or incorrect antibiotic choices due to resistant bacteria, each with deleterious consequences for patient care and public health. To approach this problem, we describe a method to rapidly isolate bacteria from whole blood using inertial microfluidics and directly determine pathogen identity and antibiotic susceptibility with hybridization-based RNA detection. Using the principle of Dean flow fractionation, bacteria are separated from host blood cells in a label-free separation method with efficient recovery of even low abundance bacteria. Ribosomal RNA detection can then be applied for direct identification of low abundance pathogens (~100 per mL) from blood without culturing or enzymatic amplification. Messenger RNA detection of antibiotic-responsive transcripts after brief drug exposure permits rapid susceptibility determination from bacteria with minimal culturing (~105 per mL). This unique coupling of microfluidic cell separation with RNA-based molecular detection techniques represents significant progress towards faster diagnostics (~8 hours) to guide antibiotic therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...