Speciation of mercury in various samples from the micro-ecosystem of East Lake by hollow fiber-liquid–liquid–liquid microextraction-HPLC-ICP-MS
Abstract
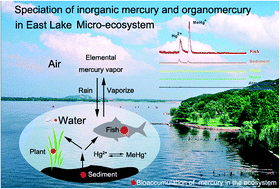
A novel method by combining hollow fiber-liquid–liquid–liquid microextraction (HF-LLLME) with HPLC-ICP-MS was developed for the speciation of inorganic mercury (Hg2+) and organomercury including methylmercury (MeHg+), ethylmercury (EtHg+) and phenylmercury (PhHg+), in the micro-ecosystem of East Lake (Wuhan, China). The factors affecting HF-LLLME were systematically investigated. Under the optimized conditions, the limits of detection for four mercury species were in the range of 2.9–5.6 ng L−1 with the relative standard deviations (c = 0.5 μg L−1, n = 7) ranging from 5.6 to 10.6%. The developed method was validated by analyzing a certified reference material of DORM-2, and the determined values were in good agreement with the certified values. The method has been applied for the speciation of mercury in five representative samples from the micro-ecosystem of East Lake including atmospheric particles, lake water, fish, plant and sediment.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analytical atomic spectrometry in China

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...