Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of mixed micellar lipid formulation of phyllanthin and piperine in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rodents†
Abstract
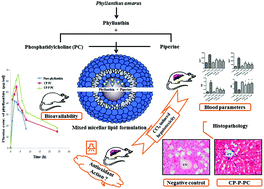
Phyllanthin, a sparingly water-soluble hepatoprotective lignin obtained from Phyllanthus amarus Schum. et Thonn. (Euphorbiaceae) possesses low bioavailability. Phyllanthin along with piperine (a nutraceutical bioenhancer) was formulated as a mixed micellar lipid formulation (MMLF) in the present study and investigated to resolve the low bioavailability and enhance hepatoprotective effects on oral administration. Hepatoprotective, antioxidant and bioavailability studies of MMLF, a complex phosphatidylcholine formulation of phyllanthin (CP–PC), phyllanthin + piperine (CP–P–PC) and its corresponding non-formulated phyllanthin have been carried out. Phyllanthin (30 mg kg−1 p.o.), CP–PC (30 mg kg−1 p.o.), CP–P–PC (30 mg kg−1 p.o.) and the reference drug silymarin (100 mg kg−1, p.o.) were administered daily to rats for 10 days, followed by liver damage by administering a 1 : 1 (v/v) mixture of CCl4 and olive oil (1 ml kg−1, i.p.) for 7 days from day 4 to day 10. The degree of protection was evaluated by determining the level of marker enzymes (SGOT and SGPT), bilirubin (TB) and total proteins (TP). Further, the effects of MMLF on lipid peroxidation (LPO), glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and glutathione reductase (GR) were estimated in liver homogenates to evaluate the antioxidant activity. Finally the concentration of phyllanthin was evaluated in plasma. EC50 values for the in vitro antioxidant assay with DPPH were found to be 19.99, 15.94 and 13.5 for phyllanthin, CP–PC and CP–P–PC, respectively. CP–P–PC (30 mg kg−1 p.o.) showed significant (p < 0.05) hepatoprotective effect by reducing the levels of serum marker enzymes (SGOT, SGPT, and TB), whereas, elevated the levels of depleted total protein (TP), lipid peroxidation and antioxidant marker enzyme activities such as, GSH, SOD, CAT, GPX, and GR. The complex MMLF normalized adverse conditions of rat livers more efficiently than the non-formulated phyllanthin. The present findings indicate that the MMLF is helpful in solving the problem of low bioavailability of phyllanthin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...