Stability and immunogenicity of hypoallergenic peanut protein–polyphenol complexes during in vitro pepsin digestion
Abstract
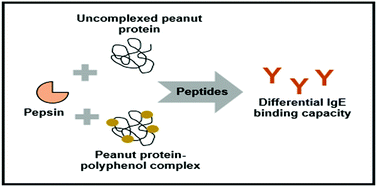
Allergenic peanut proteins are relatively resistant to digestion, and if digested, metabolized peptides tend to remain large and immunoreactive, triggering allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. In this study, the stability of hypoallergenic peanut protein–polyphenol complexes was evaluated during simulated in vitro gastric digestion. When digested with pepsin, the basic subunit of the peanut allergen Ara h 3 was more rapidly hydrolyzed in peanut protein–cranberry or green tea polyphenol complexes compared to uncomplexed peanut flour. Ara h 2 was also hydrolyzed more quickly in the peanut protein–cranberry polyphenol complex than in uncomplexed peanut flour. Peptides from peanut protein–cranberry polyphenol complexes and peanut protein–green tea polyphenol complexes were substantially less immunoreactive (based on their capacity to bind to peanut-specific IgE from patient plasma) compared to peptides from uncomplexed peanut flour. These results suggest that peanut protein–polyphenol complexes may be less immunoreactive passing through the digestive tract in vivo, contributing to their attenuated allergenicity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...