Genistein induces apoptosis by the inactivation of the IGF-1R/p-Akt signaling pathway in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
Abstract
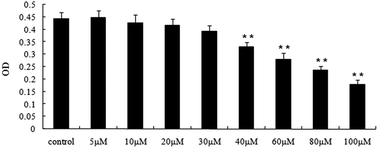
Genistein is an estrogenic soy-derived compound belonging to the isoflavone class and shows anti-cancer effects. However, the specific cell apoptosis mechanisms of genistein have not been fully understood. In this study, we investigated the specific cell apoptosis mechanisms of genistein and the potential involvement of the IGF1R-Akt-Bcl-2 and Bax-mediated pathways in human breast cancer cells in vitro. MCF-7 human breast cancer cells were treated with various concentrations of genistein, and cell proliferation was evaluated by the MTT assay. Morphological changes in treated cells were examined by Hoechst 33258 staining, and treated cells were examined by flow cytometry. The levels of IGF-1R, p-Akt, Bcl-2, and Bax protein expression and Bcl-2 and Bax mRNA expression were evaluated by western blot and RT-PCR, respectively. Genistein inhibited the proliferation of MCF-7 cells and induced cell apoptosis, as determined by Hoechst staining and flow cytometry analysis. Furthermore, genistein induced the inactivation of IGF-1R and p-Akt and downregulated the Bcl-2/Bax protein ratio. These results suggest that genistein inhibited cell proliferation by inactivating the IGF-1R-PI3 K/Akt pathway and decreasing the Bcl-2/Bax mRNA and protein expressions. Our findings help elucidate the mechanisms by which genistein may contribute to the prevention of breast cancer carcinogenesis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...