Heng-guo Wang, Shuang Yuan, Zhenjun Si and Xin-bo Zhang
Energy Environ. Sci., 2015,8, 3160-3165
DOI:
10.1039/C5EE02589C,
Communication
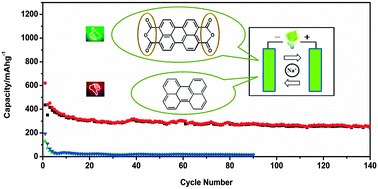
Herein we report that organic compounds comprising planar C6 ring structures and carboxylate groups can function as an excellent anode material for sodium-organic batteries. Systematic comparisons of different electrode materials including the multi-ring aromatic compounds with or without carboxylate groups are carried out, the Na insertion mechanism is proposed, and the factors determining the capacity and potential plateaus are also elucidated by experimental and theoretical analyses.