Particle suspension reactors and materials for solar-driven water splitting
Abstract
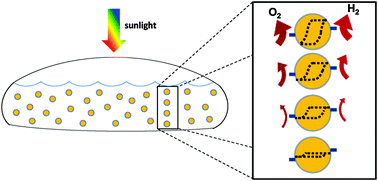
Reactors based on particle suspensions for the capture, conversion, storage, and use of solar energy as H2 are projected to be cost-competitive with fossil fuels. In light of this, this review paper summarizes state-of-the-art particle light absorbers and cocatalysts as suspensions (photocatalysts) that demonstrate visible-light-driven water splitting on the laboratory scale. Also presented are reactor descriptions, theoretical considerations particular to particle suspension reactors, and efficiency and performance characterization metrics. Opportunities for targeted research, analysis, and development of reactor designs are highlighted.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Status of Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting: Past, Present, and Future
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...