Semiconducting black phosphorus: synthesis, transport properties and electronic applications
Abstract
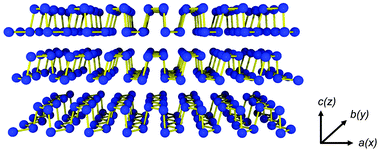
Phosphorus is one of the most abundant elements preserved in earth, and it comprises a fraction of ∼0.1% of the earth crust. In general, phosphorus has several allotropes, and the two most commonly seen allotropes, i.e. white and red phosphorus, are widely used in explosives and safety matches. In addition, black phosphorus, though rarely mentioned, is a layered semiconductor and has great potential in optical and electronic applications. Remarkably, this layered material can be reduced to one single atomic layer in the vertical direction owing to the van der Waals structure, and is known as phosphorene, in which the physical properties can be tremendously different from its bulk counterpart. In this review article, we trace back to the research history on black phosphorus of over 100 years from the synthesis to material properties, and extend the topic from black phosphorus to phosphorene. The physical and transport properties are highlighted for further applications in electronic and optoelectronics devices.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2D Transition Metal Dichalcogenide (TMD) Nanosheets
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...