Basic concepts of quantum interference and electron transport in single-molecule electronics
Abstract
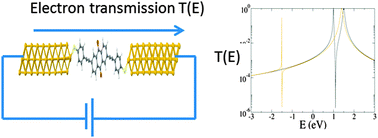
This tutorial outlines the basic theoretical concepts and tools which underpin the fundamentals of phase-coherent electron transport through single molecules. The key quantity of interest is the transmission coefficient T(E), which yields the electrical conductance, current–voltage relations, the thermopower S and the thermoelectric figure of merit ZT of single-molecule devices. Since T(E) is strongly affected by quantum interference (QI), three manifestations of QI in single-molecules are discussed, namely Mach–Zehnder interferometry, Breit–Wigner resonances and Fano resonances. A simple MATLAB code is provided, which allows the novice reader to explore QI in multi-branched structures described by a tight-binding (Hückel) Hamiltonian. More generally, the strengths and limitations of materials-specific transport modelling based on density functional theory are discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Molecular Wires


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...