A correlation between thermodynamic properties, thermal expansion and electrical resistivity of Ag–28% Cu nanopowders processed by the mechanical alloying route
Abstract
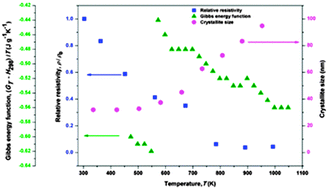
Thermodynamic properties, thermal expansion and electrical resistivity of the Ag–28% Cu nanopowders processed by the mechanical alloying route have been investigated in the temperature range from ambient to 1048 K. The thermodynamic properties represented by the relative enthalpy, the specific heat capacity, the relative entropy and the Gibbs energy function obtained from drop calorimetric measurements have been used to reveal the occurrence of the micro-relaxation process, as well as of the correlative effects of decomposition and growth processes. On the basis of the results, the parameters that favour stable nanostructured systems in Ag–28% Cu powders synthesized by the mechanical alloying route have been identified. The correlation of the energetic parameters with thermal expansion and electrical resistivity in mechanical alloyed nanocrystalline powders with the eutectic composition is discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent advances in the chemical physics of nanoalloys

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...