Metastable alloy nanoparticles, metal-oxide nanocrescents and nanoshells generated by laser ablation in liquid solution: influence of the chemical environment on structure and composition
Abstract
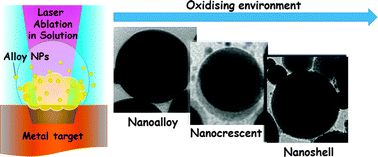
Alloy nanoparticles are characterized by the combination of multiple interesting properties, which are attractive for technological and scientific purposes. A frontier topic of this field is nanoalloys with compositions not thermodynamically allowed at ordinary temperature and pressure (i.e. metastable), because they require out-of-equilibrium synthetic approaches. Recently, laser ablation synthesis in solution (LASiS) was successfully applied for the realization of metastable nanoalloys because of the fast kinetics of nanoparticle formation. However, the role played by the chemical environment on the final composition and structure of laser generated nanoalloys still has to be fully elucidated. Here, we investigated the influence of different synthetic conditions on the LASiS of metastable nanoalloys composed of Au and Fe, such as the use of water instead of ethanol, the bubbling of inert gases and the addition of a few vol% of H2O2 and H2O. The two elements showed different reactivity when LASiS was performed in water instead of ethanol, while minor effects were observed from bubbling pure gases such as N2, Ar and CO2 in the liquid solution. Moreover, the plasmonic response and the structure of the nanoalloys were sensibly modified by adding H2O2 to water. We also found that nanoparticle production is dramatically influenced just by adding 0.2% of H2O in ethanol. These results suggest that the formation of a cavitation bubble with long lifetime and large size during LASiS is useful for the preservation of the metastable alloy composition, whereas an oxidative environment hampers the formation of metastable alloy nanoparticles. Overall, by acting on the type of solvent and solutes, we were able to switch from a traditional synthetic approach for the composition of Au–Fe nanoalloys to one using a reactive environment, which gives unconventional structures such as metal@iron-oxide nanoshells and nanocrescents of oxide supported on metal nanospheres. These results expand the knowledge about the mechanism of the formation of nanoalloys using LASiS and show how to obtain multielement nanoparticles of enormous interest for nanomedicine, plasmonics, magneto-plasmonics and catalysis.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent advances in the chemical physics of nanoalloys

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...