α-Aminoisobutyric acid incorporation induces cell permeability and antiviral activity of HIV-1 major homology region fragments†
Abstract
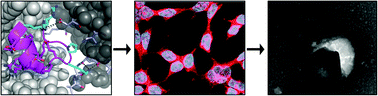
The design of a cell penetrating antiviral peptide, which is derived from the major homology region of HIV-1 capsid protein and includes the non-coded α-aminoisobutyric acid, provides functional evidence for the role of the conserved region in the HIV assembly process and demonstrates the correlation between conformational stability and cellular permeability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...