PLA-poloxamer/poloxamine copolymers for ligament tissue engineering: sound macromolecular design for degradable scaffolds and MSC differentiation†
Abstract
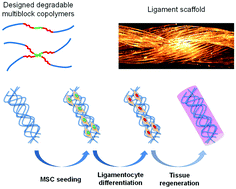
The treatment of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) failures remains a current clinical challenge. The present study aims at providing suitable degradable scaffolds for ligament tissue engineering. First, we focus on the design and the evaluation of poly(lactide)/poloxamer or poly(lactide)/poloxamine multiblock copolymers selected and developed to have suitable degradation and mechanical properties to match ACL repair. In the second part, it is shown that the copolymers can be processed in the form of microfibers and scaffolds consisting of a combination of twisted/braided fibers to further modulate the mechanical properties and prepare scaffold prototypes suitable for ligament application. Finally, after assessment of their cytocompatibility, the polymer scaffolds are associated with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). MSC differentiation toward a ligament fibroblast phenotype is promoted by a dual stimulation including an inductive culture medium and cyclic mechanical loads. RT-qPCR analyses confirm the potential of our scaffolds and MSCs for ACL regeneration with upregulation of some differentiation markers including Scleraxis, Tenascin-C and Tenomodulin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...