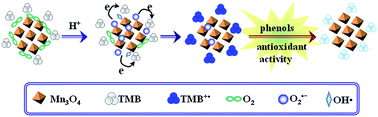
In this paper, we successfully synthesized novel Mn3O4 nano-octahedrons using a simple hydrothermal method and demonstrated that the prepared Mn3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) exhibited highly intrinsic oxidase-like activity and could catalyze the reaction of TMB, ABTS and OPD to produce a typical color reaction in the absence of H2O2 within minutes. Compared with other non-noble metal NPs oxidase nanozymes, the affinity of Mn3O4 NPs to TMB was increased by at least 35% according to the Km values. It was deduced that O2˙− and few OH˙ radicals were produced during the catalytic reaction. Then, the addition of twelve phenols to the TMB–Mn3O4 NP system led to the fading of the solution by different degrees based on the antioxidant activity of the phenols. Thus, preliminary assessment of the antioxidant ability of twelve phenols using TMB decolorization assays was realized based on the excellent oxidase-like properties of the Mn3O4 NPs. Finally, under the optimum conditions, visual determination of tannic acid (TA) was realized and the detection limit was 19 nM with a linear range from 0.05 to 1.4 μM. The proposed method was successfully used to determine TA in tea samples.