Tissue distribution of 10-methoxycamptothecin and its metabolite 10-hydroxycamptothecin in rats by a RP-HPLC method with fluorescence detection/UV detection
Abstract
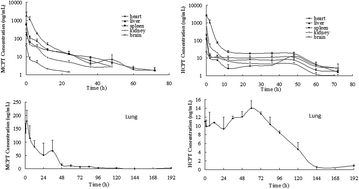
Both 10-methoxycamptothecin (MCPT) and 10-hydroxycamptothecin (HCPT) are natural derivatives of camptothecin (CPT) isolated from Camptotheca acuminata, possessing broad-spectrum antitumor activity. HCPT was identified as a major metabolite of MCPT in rats. In the present study, liquid chromatography coupled with a fluorescence detector (or a UV detector) was used to study the tissue distribution of MCPT and its metabolite HCPT in rats after i.v. administration (5 mg kg−1). The results indicated that MCPT was rapidly absorbed and diffused into all the tissues sampled (heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, and brain) after i.v. administration. MCPT was accumulated at very high levels in lung tissues, which can be quantified until 120 h, and the concentration was up to 1000 times higher than that found in the plasma sample. The AUC0–∞ of MCPT in lung tissues was 3888.45 ± 203.59 μg h mL−1, which is about 650 and 40 000 times that found in the liver and brain tissues. The level of MCPT reached its maximum right after i.v. administration then declined in the liver, spleen, kidney, heart, and brain tissues and was detectable until 72 h in liver and heart tissues, 48 h in the spleen and kidney tissues, and 24 h in the brain tissues. HCPT showed similar concentration–time profiles to MCPT, wherein the HCPT concentration was relatively steady from 12 h to 48 h and can be quantified in the lung tissues until 120 h and in the liver, spleen, kidney, heart and brain tissues until 72 h. The maximum concentration of HCPT was very low, whereas it remained steady from 2 h until 48 h, giving an AUC0–∞ much higher than that of MCPT in brain and also higher than the AUC0–∞ of HCPT in heart and spleen tissues.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...