Novel l-lactic acid biosensors based on conducting polypyrrole-block copolymer nanoparticles†
Abstract
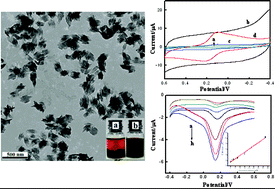
The development of advanced nanomaterials for the highly efficient electrical detection of biological species has attracted great attention. Here, novel polypyrrole-Pluronic F127 nanoparticles (PPy-F127 NPs) with conducting and biocompatibility properties were synthesized and used to construct a L-lactic acid biosensor that could be applied in biochemical assays. The PPy-F127 NPs were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), elemental analysis and UV-vis spectroscopy. Lactate oxidase (LOx) structure variation on the PPy-F127 NPs was investigated by circular dichroism (CD). The cyclic voltammetric results indicated that LOx immobilized on the PPy-F127 NPs exhibited direct electron transfer reaction with a formal potential value (E0′) of 0.154 V vs. SCE. Moreover, the biosensor had good electrocatalytic activity toward L-lactic acid with a wide linear range (0.015–37.5 mM) and a low detection limit of 0.0088 mM. The regression equation was I (μA) = 0.02353c (mM) + 1.4135 (R2 = 0.9939). The L-lactic acid biosensor had a good anti-interference property towards uric acid (UA), ascorbic acid (AA), glucose and cysteine. The idea and method provide a promising platform for the rapid development of biosensors that can be used in the detection of biological species.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...