Temperature- and pH-tunable plasmonic properties and SERS efficiency of the silver nanoparticles within the dual stimuli-responsive microgels†
Abstract
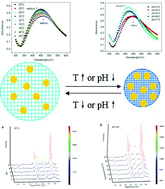
The silver nanoparticle (AgNP)-loading microgels with an interpenetrating polymer network structure composed of separately cross-linked poly(acrylic acid) and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) were prepared through an in situ reduction reaction of silver ions coordinated into their networks. The temperature- or pH-dependent hydrodynamic diameters measured using dynamic laser light scattering show that the hybrid microgels produced has dual pH and temperature stimuli-responsive properties with little mutual interference between the temperature- and pH-responsive components. The localized surface plasmon resonance wavelength of the AgNPs inside the microgels can be reversibly tuned with temperature changing from 20 °C to 45 °C or pH values changing from 3.0 to 7.0. When the hybrid microgels were used as the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates for probing minute amounts of 4-mercapto benzoic acid in an aqueous solution, its SERS intensity is remarkably increased with pH value lowering from 7.0 to 3.0 or temperature rising from 20 °C to 45 °C. If the two stimuli are simultaneously exerted, the SERS intensity is greatly elevated. The temperature and pH value measuring results show that the hybrid microgels are able to be utilized as SERS microsensors for measuring both pH value and the temperature of their surroundings.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...