Topography-dependent antibacterial, osteogenic and anti-aging properties of pure titanium†
Abstract
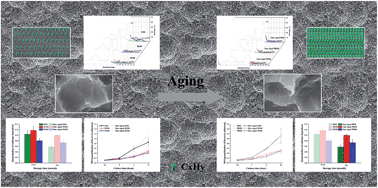
After nearly half a century of development under the guidance of the osseointegration theory, the major dilemmas for current implant dentistry are the implant associated infection and insufficient osseointegration. Moreover, biological aging of titanium (Ti) implants also brings great uncertainty to clinical results. In the present study, a novel nano–micro-hierarchical topography pattern is created by sandblasting and dual acid-etching on a Ti surface. The physico-chemical properties of the surfaces were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, contact angle measurement, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. The effects of the hierarchical surfaces on osteoprogenitor cell growth and bacterial activities were separately evaluated. The optimized nano–micro-hierarchical Ti surface exhibits surprisingly topography-dependent antibacterial capacity via inhibiting bacterial adhesion of several species in the early stage and better osteogenesis ability than the microscaled surface. Aging studies demonstrate that, compared with the surface with a microscale structure, the nano–micro-hierarchical Ti surface has greater anti-aging ability manifested as being more capable to retain hydrophilicity and bioactivity during aging. Furthermore, the present study reveals that the biological aging of the Ti implant is attributed to two decisive factors during the aging period: the progressively thickened amorphous TiO2 layer by autoxidation and the unavoidable accumulation of hydrocarbons on the Ti implant surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...