Rapid, microwave-assisted synthesis of Gd2O3 and Eu:Gd2O3 nanocrystals: characterization, magnetic, optical and biological studies†
Abstract
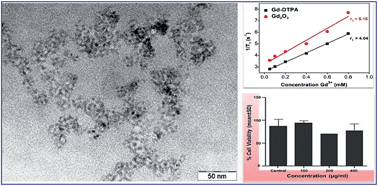
Ultra-small crystals of undoped and Eu-doped gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3) were synthesised by a simple, rapid microwave-assisted route, using benzyl alcohol as the reaction solvent. XRD, XPS and TEM analysis reveal that the as-prepared powder material consists of nearly monodisperse Gd2O3 nanocrystals with an average diameter of 5.2 nm. The nanocrystals show good magnetic behaviour and exhibit a larger reduction in relaxation time of water protons than the standard Gd–DTPA complex currently used in MRI imaging. Cytotoxicity studies (both concentration- and time-dependent) of the Gd2O3 nanocrystals show no adverse effect on cell viability, evidencing their high biological compatibility. Finally, Eu:Gd2O3 nanocrystals were prepared by a similar route and the red luminescence of Eu3+ activator ions was used to study the cell permeability of the nanocrystals. Red fluorescence from Eu3+ ions observed by fluorescence microscopy shows that the nanocrystals (Gd2O3 and Eu:Gd2O3) can permeate not only the cell membrane but can also enter the cell nucleus, rendering them candidate materials not only for MRI imaging but also for drug delivery when tagged or functionalized with specific drug molecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...