Dye adsorption and decomposition on two-dimensional titanium carbide in aqueous media†
Abstract
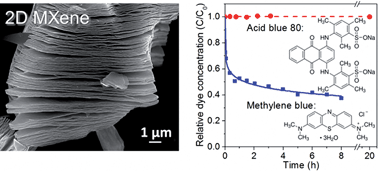
Recently a large family of two-dimensional (2D) layered early transition metal carbides and carbonitrides – labelled MXene – possessing metallic conductivity and hydrophilic surfaces was discovered. Herein we report on the adsorption and photocatalytic decomposition of organic molecules in aqueous environments containing Ti3C2Tx, a representative of the MXene family. This material possesses excellent adsorption toward cationic dyes, best described by a Freundlich isotherm. We also found that the material may undergo structural changes in aqueous media.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...