Microwave-synthesized poly(ionic liquid) particles: a new material with high electrorheological activity
Abstract
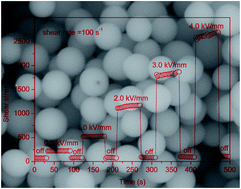
Hydrophobic poly(ionic liquid) particles are synthesized by a microwave-assisted dispersion polymerization method and their electro-responsive characteristic is investigated as a new water-free polyelectrolyte-based electrorheological (ER) system. Structure characterization shows that the poly(ionic liquid) particles are uniform microspheres with a narrow size distribution of ∼1.8 μm and a low density of ∼1.62 g cm−3. Under electric fields, the fluid of poly(ionic liquid) particles in silicone oil shows low current density but high ER activity including small off-field viscosity, large field-induced shear stress and storage modulus, and stable flow curves in a wide shear rate region. The ER effect increases with particle content. The typical shear stress is ∼2500 Pa at 4 kV mm−1 and 100 s−1, which is ∼30 times as high as the off-field shear stress. Dielectric spectra analysis indicates that the high ER activity can be attributed to strong dielectric polarizability and adequate polarization response induced by the high-density of cation/anion parts in poly(ionic liquid) particles. The ER activity also depends on the type of cation/anion parts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...